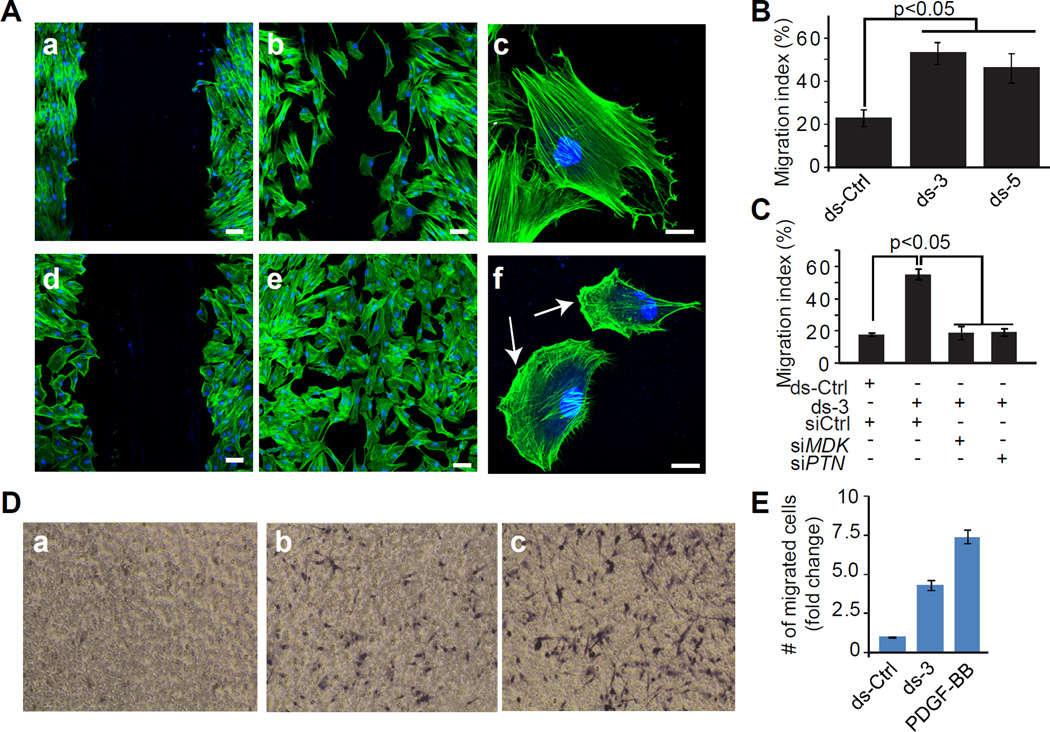
Figure 7. Effect of SENCR knockdown in a scratch wound assay of cell migration.
(A) HCASMC were transfected with ds-Ctrl (panels a–c) or ds-SENCR-3 (panels d-f) for 72 hr after which a scratch wound was created and cell migration assessed in quiescent (panels a, d) HCASMC or in similar cells stimulated for 12 hr with 10% FBS (panels b, c, e, f). Cells were stained with phalloidin (red) and DAPI (blue). Bars are 25 µm in panels a, b, d, and e and 10 µm in panels c and f. Arrows in panel f denote lamellipodia. (B) Quantitative measure of the area of the wound occupied by dsRNA-transfected HCASMC 12 hrs following serum stimulation. (C) Same experiment as in B only HCASMC were transfected simultaneously with a control siRNA (siCtrl) or an siRNA to one of two pro-migratory genes. Each siRNA reduced level of MDK or PTN mRNA by more than 80% (Figure V in the online only Data supplement). (D) Effect of SENCR knockdown on HCASMC migration in a Boyden chamber. Cells were transfected with ds-Ctrl (a), ds-3 (b) or 25 ng/ml PDGF-BB (c) for 6 hr and the fold change in number of cells migrating through the porous membrane quantitated (E). The data reflect cell counts from 5 independent fields.