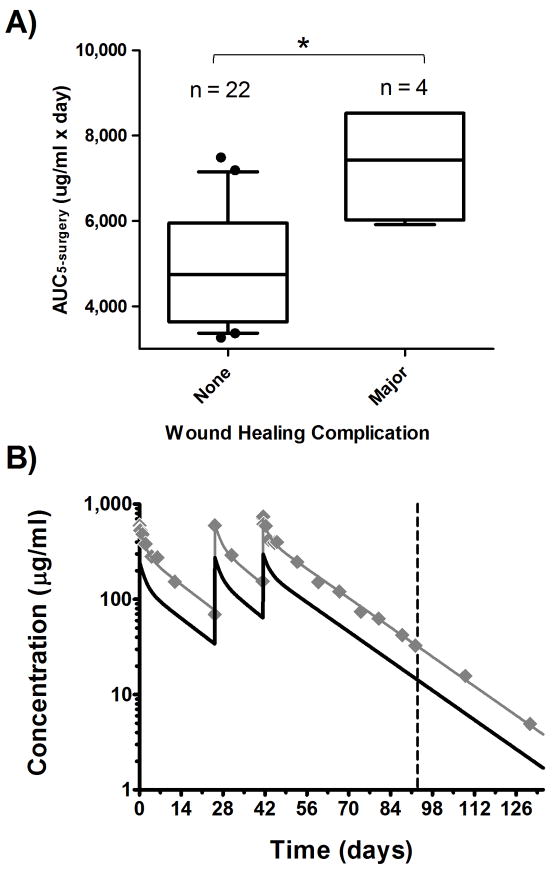
Figure 4.
A, The odds of a major wound complication increased by 3.1-fold (*95% CI: 1.1-9.1; p = 0.03) for every 1000 μg/ml*day increase in AUC5–surgery (box: interquartile range; whiskers: 90% CI; filled circles: data residing outside 90% CI). In B, observed bevacizumab concentration-time data (filled diamonds) are shown for an obese 12-year old boy with a BMI of 40.6 kg/m2 who experienced a major wound healing complication (surgery on day 93; vertical dashed line). Pharmacokinetic simulations indicate that 15 mg/kg IBW-based dosing (solid black line) decreases bevacizumab AUC5–surgery from 8,529 μg/ml*day to 3,756 μg/ml*day compared to simulation using the actual body weight dosing (solid gray line), effectively reducing the odds of major wound complication by almost 300-fold for this child.