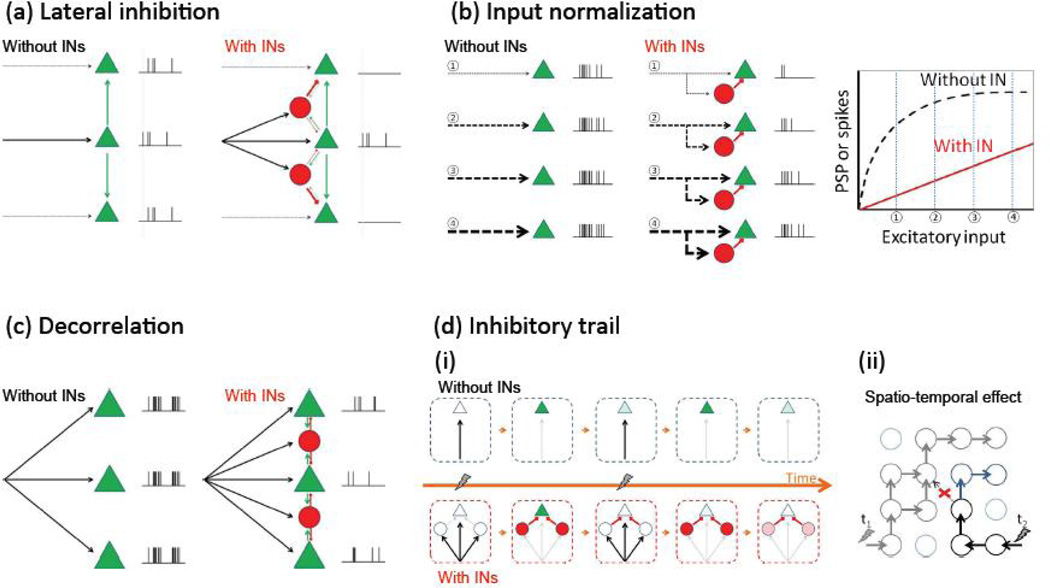
Figure 2.
Functional roles of INs. (a) Lateral inhibition. (b) Input normalization. (c) INs decorrelate PC spiking. (d) Inhibitory trail reduces response to a second input. Lightning symbols indicate input along arrows. (ii) Simple temporal effect. Green triangles represent PCs and red circles represent INs. (ii) example of spatio-temporal effect. Here circles represent modules containing both INs and PCs, and arrows the spread of excitation; because of the inhibitory trail stimulation of a pathway at t1, shortly before stimulation of another path at t2 blocks the progress of the latter activity at the red cross and directs it instead to the blue direction.