Fig. 4.
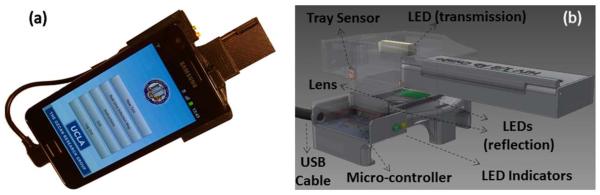
(a) The universal Rapid Diagnostic Test (RDT) reader installed on an Android phone [9]. The light-weight (65 g) opto-mechanical attachment can be repeatedly attached/detached to the cellphone body without the need for fine alignment and modification. (b) Schematic of the designed optical RDT reader attachment. RDT tray works as a mechanical adaptor to insert various RDT types into the same cellphone based reader attachment. The tray sensor is a conductive component that is used to sense the insertion of the tray and ensures the proper operation of the device. Controlled using a simple micro-chip, the illumination LEDs uniformly illuminate the RDT of interest that is imaged by the cell-phone camera through an additional plano-convex lens. Reproduced with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry.
