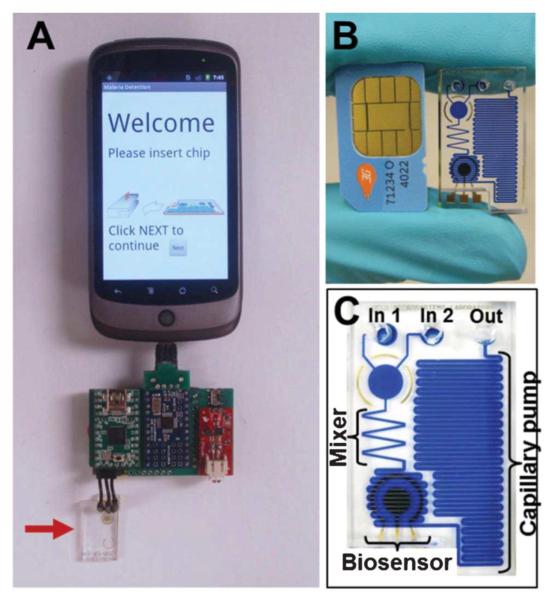
Fig. 5.
(A) Assembled smartphone-based electrochemical sensor [15]. The arrow indicates the microfluidic chip. (B) Photograph of the chip and a mobile phone SIM card for comparison. (C) An enlarged image of the chip with labeled components. The channels are filled with a dye for improved visualization of the fluidic network. Reproduced with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry.