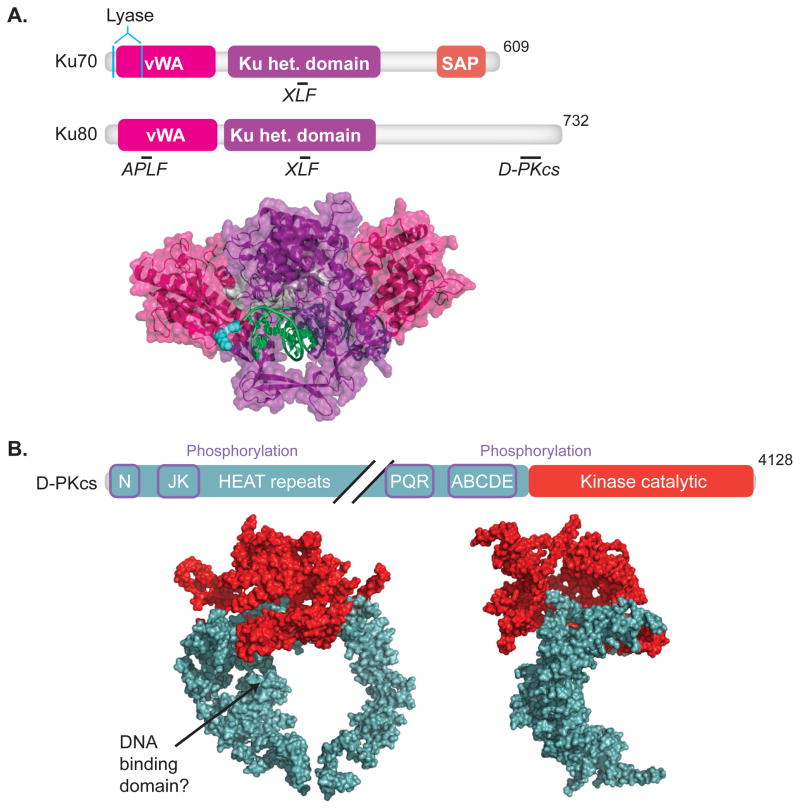
Fig.1. DNA-PK.
Domain maps indicating sites of protein-protein interactions, underlined, interacting proteins, italics, (upper panel) and crystal structures (lower panel) are shown for (A) Ku70 and Ku80 (1JEY)[16] and (B) DNA-PKcs, front and side view (3KGV)[21]. Colors in crystal structures correspond to features in domain maps. (A)Domains of Ku70 include the vWA (von Wilebrand associated) domain, pink, the heterodimerization domain (het.), purple, and SAP (C-terminal SAF-A/B, Acinus and PIAS) domain, orange. Residues important for lyase activity are located in Ku70, cyan [55, 56]. Domains of Ku80 include the vWA domain, and het. domain. Ku 70/80 interactions with APLF [14], DNA-PKcs [11], and XLF [15] are shown. (B) Domains of DNA-PKcs include an N-terminal domain, a kinase catalytic domain, red. Diagonal black lines denote a break in the domain map. Sites of phosphorylation, purple boxes, and HEAT (Huntington elongation factor 2, A subunit of protein phosphatase 2A and TOR1) repeats are indicated.