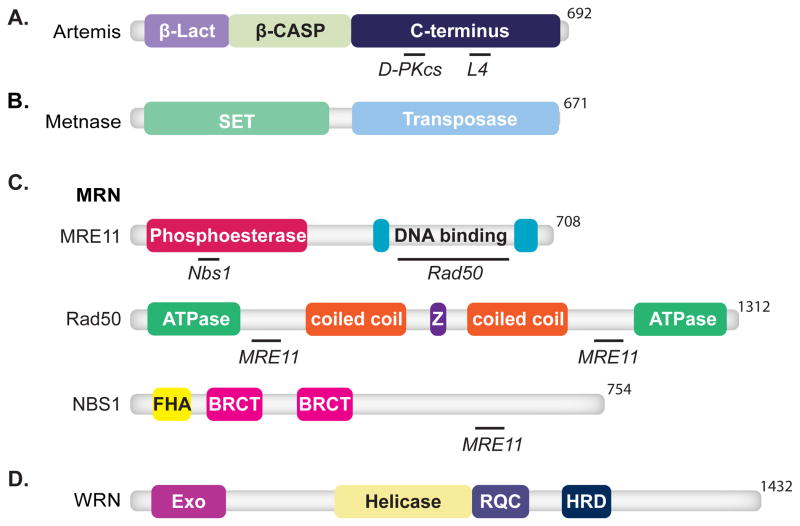
Fig. 5. Nucleases.
Features of domain maps are as indicated in Figure 1. (A) Artemis consists of an N-terminal metallo-β-lactamase (β-Lact) domain, purple, and a metallo-β-lactamase-associated CPSF Artemis SNM1 PSO2 (β-CASP) domain, light green, and a C-terminal domain, dark blue. Artemis interacts with DNA-PKcs (D-PKcs) [106, 107] and ligase IV (L4) [109, 110]. (B) Metnase is composed of a N-terminal Su(var) Ez and Trithorax (SET) domain, light green, and a transposase domain, light blue. (C) MRN is composed of MRE11, Rad50, and NBS1. Mre11 contains phosphoesterase, red, and DBDs, cyan. Mre11 interacts with Nbs1 and Rad50 [154]. Domains of Rad50 include ATPase domains, light green, CC domains, orange, and zinc finger domain (Z), purple. Rad50 associates with Mre11 [154]. NBS1 consists of an FHA domain, yellow, and BRCT domains, pink. NBS1 also associates with Mre11 [154]. (D) WRN is composed of a N-terminal exonuclease domain, fuchsia, a helicase domain, yellow, the RecQ carboxy-terminal (RQC) domain, purple, and a helicase and RNase D C-terminal (HRDC) domain, dark blue.