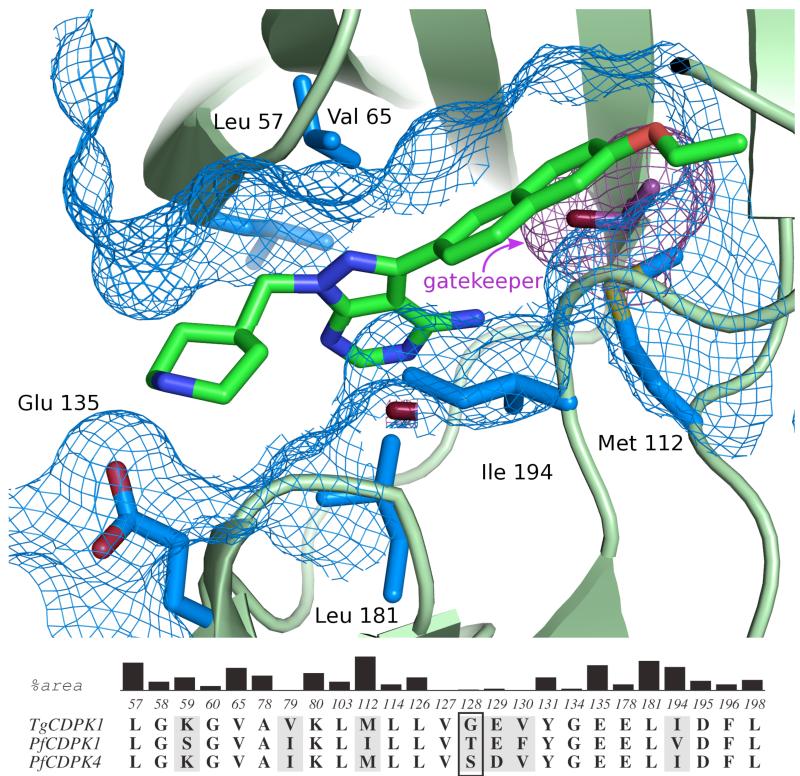
Figure 2.
(A) Structure of a pyrazolopyrimidine-based inhibitor (17j) bound to the ATP-binding site of TgCDPK1. The six residues that contribute the largest surface area to the inhibitor binding site are show in blue. The gatekeeper residue is shown in purple. Residue numbering refers to that of TgCDPK1. (B) Conservation of residues making up the CDPK active site. The residues shown are those within 5 Å of bound inhibitor 17j as observed in complex with TgCDPK1 (PDB 3s×9). The black vertical bars show the relative contributions of atoms in each reside to the surface area of the binding site in TgCDPK1. Residues that are shaded grey are not conserved between TgCDPK1, PfCDPK1, and PfCDPK4. The gatekeeper residue (Gly128 in TgCDPK1 and Ser147 in PfCDPK4) is boxed.