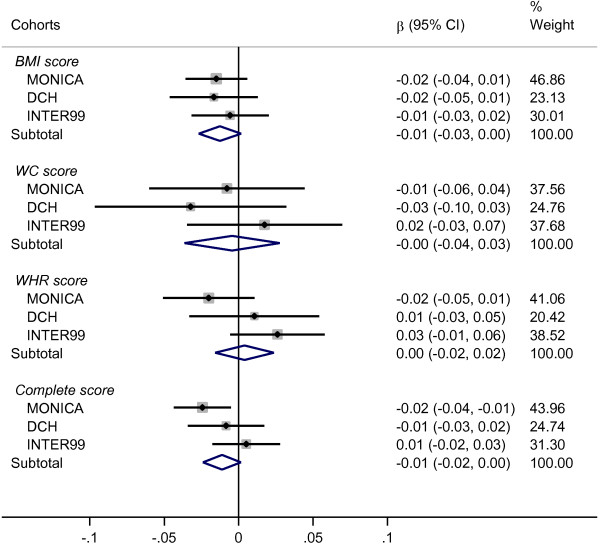
Figure 1.
Interaction between genetic predisposition scores and dietary ascorbic acid in relation to change in body weight. Abbreviations: BMI score, sum of body mass index associated risk-alleles; WC score, sum of waist circumference associated risk-alleles; WHR score, sum of waist-hip ratio associated risk-alleles; Complete score, sum of SNP associated to all three phenotypes. Results presented as annual weight change (kg/year) effect-modification for each additional risk-allele per 100 mg/day higher ascorbic acid intake. The study-specific SNP-score × ascorbic acid interactions were calculated using linear regression and corresponding meta-analysis results were derived using a fixed effect approach, where the effect-estimates where weighted by the inverses of their variances (% weight). The results were adjusted for baseline measure of body weight, height, sex, age, smoking status, alcohol consumption, physical activity, education and menopausal status for women.