Figure 3.
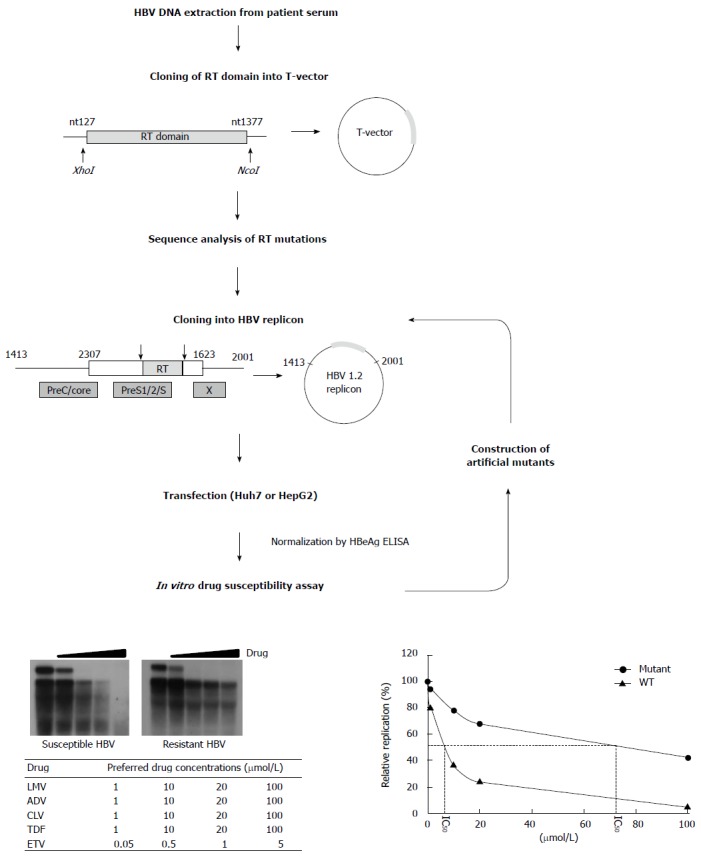
Scheme for in vitro phenotypic validation of drug-resistant hepatitis B virus. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA is purified from patient serum, and the sequence of RT mutations is analyzed. After cloning into replication-competent HBV replicons, each mutant is transfected into hepatoma cell lines followed by Southern blot (or real time polymerase chain reaction) analysis. The IC50 (μmol/L) value is obtained by quantification of replication ability and curve-fitting. To characterize the specific mutation(s) conferring resistance to antiviral drugs, each artificial mutant must be constructed and individually tested.
