Figure 3.
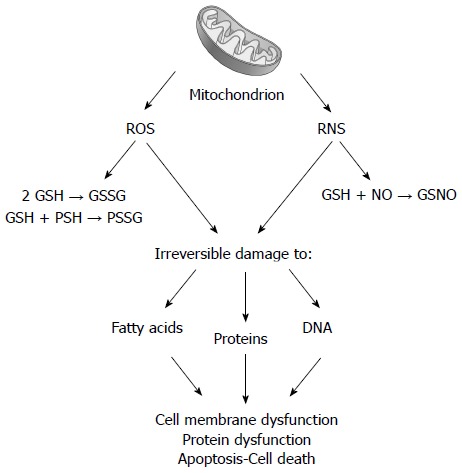
Following chronic cholestasis, liver mitochondrial impairment is associated with increased delivery of reactive oxygen species and reactive nitrogen species. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) promotes the oxidation of glutathione (GSH to GSSG) and of protein sulfhydryls (PSH to PSSG). Reactive nitrogen species (RNS) favors the formation of nitrosothiols (GSNO). Both steps are responsible for irreversible damage to lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, ultimately leading to membrane and protein alteration.
