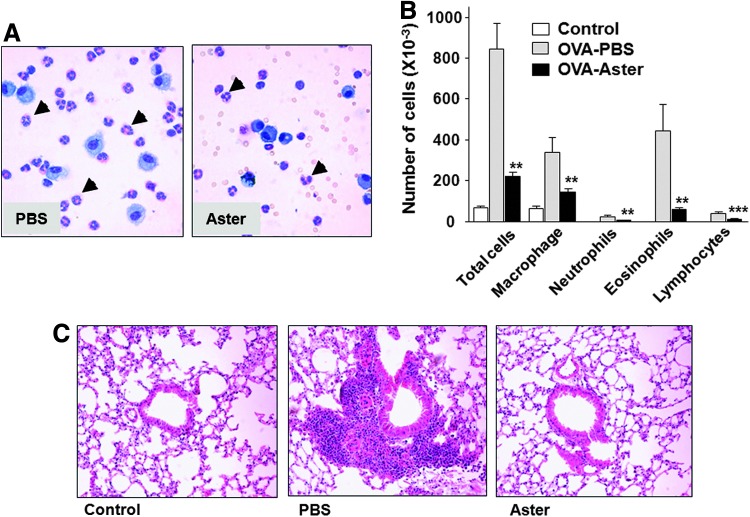
FIG. 2.
Decreased numbers of cells in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid and histopathological changes in ovalbumin (OVA)-challenged mice treated with an ethanol extract of A. yomena. (A) Representative photographs of a differential cell count by Diff-Quik staining. Bronchoaveolar lavage fluid (BALF) cells from phosphate-buffered saline–treated (PBS) or A. yomena extract–treated (Aster) OVA-challenged mice were centrifuged onto microscope slides and stained with Diff-Quik. Leukocytes were classified as macrophages, lymphocytes, neutrophils, or eosinophils (arrow head). Magnification, ×400. (B) Differences between OVA-challenged mice treated with PBS (gray) and those treated with A. yomena extract (black) were evaluated by an unpaired, two-tailed Student's t-test (**P<.01, ***P<.001). Data are expressed as means±SEM (n=5–8). (C) Lung histology was examined in control mice and PBS-treated or A. yomena extract–treated OVA-challenged mice by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of paraffin-embedded sections. Magnification, ×200. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/jmf