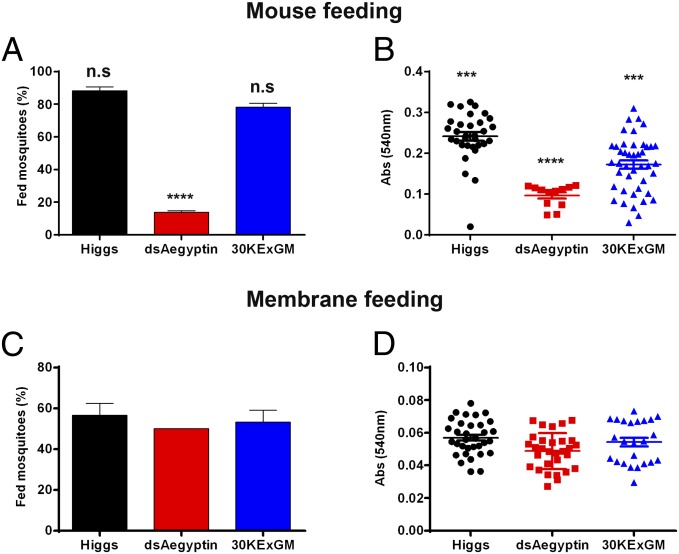
Fig. 6.
Feeding success of transgenic mosquitoes on mice and artificial membranes. (A) Reduced levels of Aegyptin significantly lowered the feeding success of mosquitoes on anesthetized mice. Percentages of successful feeding were analyzed by using a χ2 test. (B) Transgenic mosquitoes expressing dsRNAi against Aegyptin mRNA had significantly smaller blood content in their abdomens. Blood meal size (expressed as OD540nm units) ingested by mosquitoes that fed on mice was quantified by measuring the total hemoglobin content using Drabkin’s reagent as described in Materials and Methods. (C) dsAegyptin mosquitoes did not differ in their feeding success compared with controls when fed on an artificial membrane and a bloodmeal lacking collagen and collagen-induced platelet activation and aggregation. (D) Measurement of blood meal size revealed that dsAegyptin and 30KExGM had ingested similar amounts of blood when fed on artificial membrane system. Results were analyzed by using a χ2 test with 95% confidence interval. ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001. n.s, not significant.