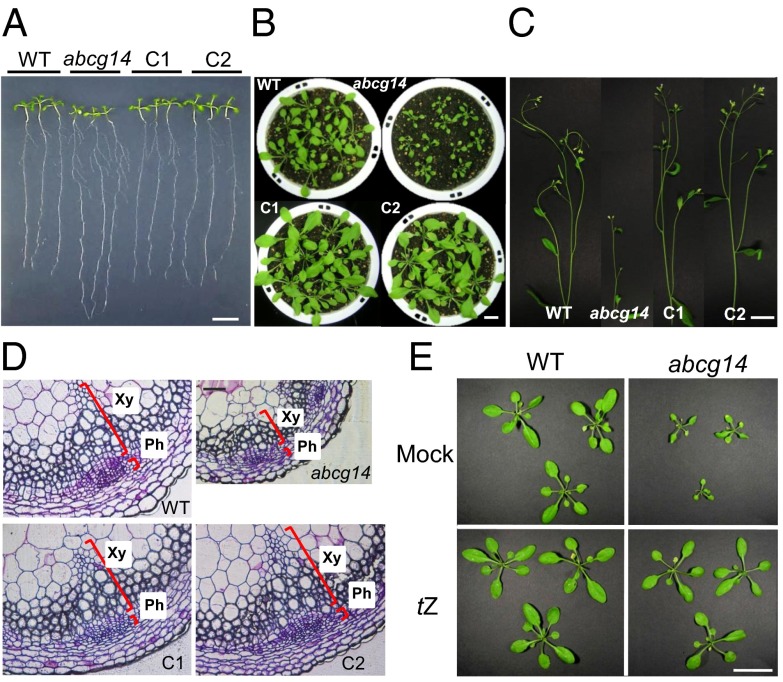
Fig. 1.
Shoot growth retardation of atabcg14 and its recovery by tZ application. (A) Altered shoot-to-root ratio of atabcg14 knockout (abcg14) compared with the wild type. Plants were grown on MGRL-agar medium under short-day conditions (8 h/16 h, light/dark). (Scale bar, 1 cm.) (B and C) Leaves (B) and inflorescence stems (C) of 28-d-old wild-type (WT), abcg14, and complementation lines (C1 and C2). (Scale bar, 4 cm.) Note that abcg14 exhibits severely retarded shoot growth. Pictures were taken separately at the same time and composed into a single image. (D) Transverse sections of the inflorescence stems of wild-type, abcg14, and complementation lines. Sections were taken at the base of the stem of 35-d-old plants and stained with toluidine blue. Ph, phloem; Xy, xylem. (Scale bar, 80 µm.) (E) Leaves of wild-type and abcg14 plants sprayed with 0.1% DMSO (solvent control) solution (Mock, Upper) or 1 µM tZ (Lower) once a day for 21 d starting from 10 d after sowing. (Scale bar, 4 cm.)