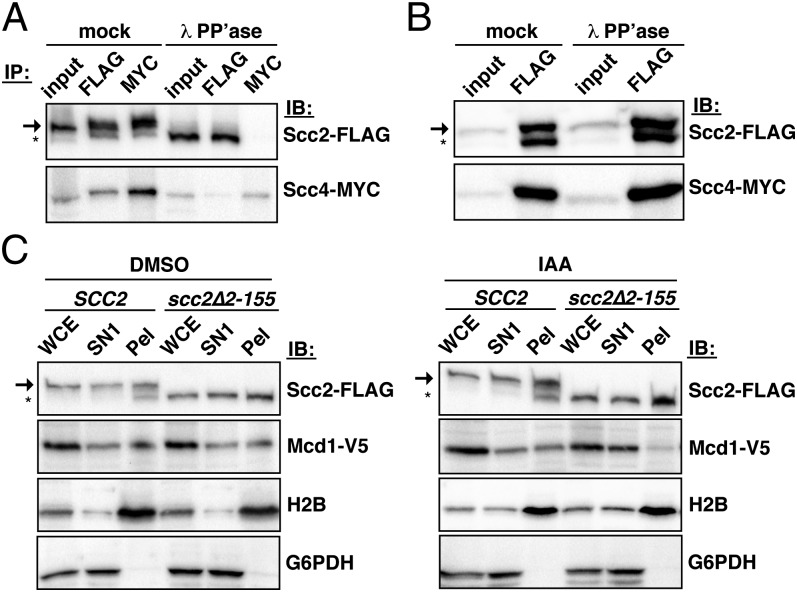
Fig. 4.
Scc2 cleavage affects its interaction with Scc4 and Mcd1 chromatin association. (A) Reciprocal coimmunoprecipitations were performed in λ phosphatase- or mock-treated extracts of Scc2-FLAG Scc4-13MYC cells (1891-32C). The arrow and asterisk indicate full-length and cleaved Scc2, respectively. (B) Scc2-FLAG immunopurified from Scc2-FLAG Scc4-13MYC cells (1891-32C) was subsequently either mock treated or treated with phosphatase. Samples were then immunoblotted with FLAG or MYC to determine the ability of phosphatase-treated samples to coimmunoprecipitate Scc4-13MYC. (C) Cells expressing plasmid-borne Scc2-FLAG or Scc2∆2-155-FLAG and chromosomal Scc2 fused to an auxin-inducible domain (JWY214 and JWY215, respectively) were treated with auxin or vehicle only (DMSO) as described in the text and then subjected to fractionation. Immunoblots of WCE, SN1, and pellet fractions are shown for the indicated proteins.