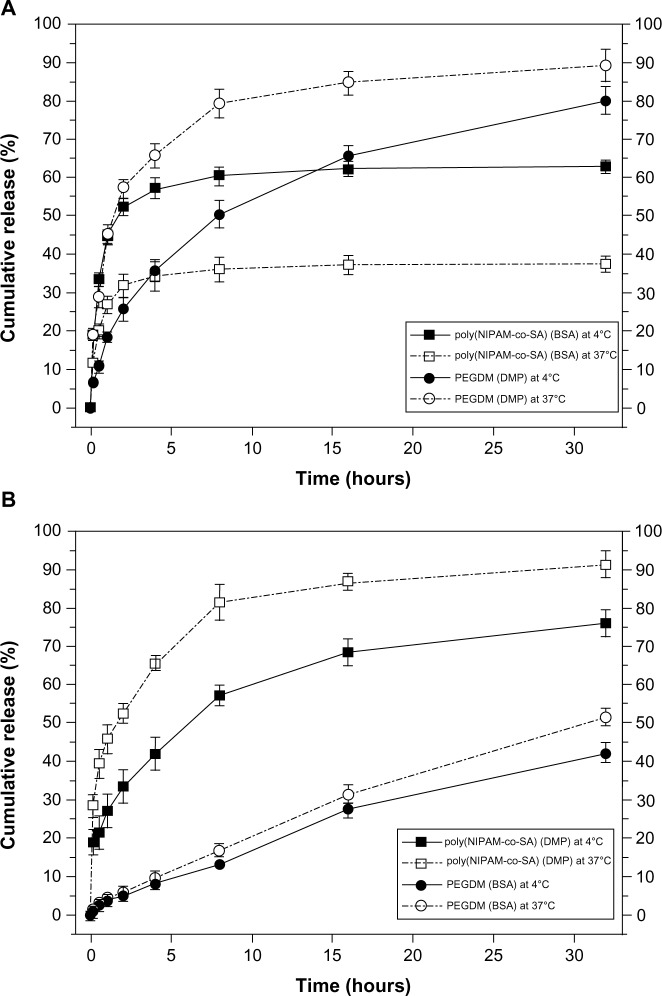
Figure 7.
Decoupled in vitro drug release kinetics from the dual drug-loaded bicompartmental nanofibers composed of poly(NIPAM-co-SA) and PEGDMA compartments at various temperatures.
Notes: Two different sets of the dual drug-loaded bicompartmental nanofibers were prepared: (A) a BSA-loaded poly(NIPAM-co-SA) compartment and a DMP-loaded PEGDMA compartment; and (B) a DMP-loaded poly(NIPAM-co-SA) compartment and a BSA-loaded PEGDMA compartment. The different sets of the dual drug-loaded nanofiber solutions were maintained in a suspension state at 4°C or 37°C to observe the temperature-controlled drug release. The BSA from the BSA-loaded poly(NIPAM-co-SA) compartment was released at a slower rate at 37°C compared to 4°C because aggregation of the poly(NIPAM-co-SA) chains at 37°C caused the hydrated pore size of the poly(NIPAM-co-SA) compartment to become smaller, trapping BSA within the physically-crosslinked poly(NIPAM-co-SA) compartment.
Abbreviations: poly(NIPAM-co-SA), poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-stearyl acrylate); BSA, bovine serum albumin; PEGDMA, polyethylene glycol dimethacrylates; DMP, dexamethasone 21-phosphate.