Figure 1.
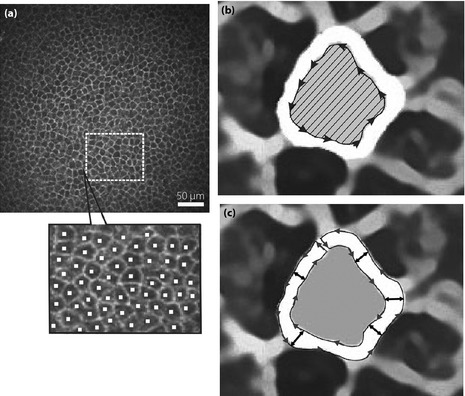
(a) The determination of the density of corneal epithelial basal cells (CEBCs). At first, the region of interest (ROI; mm2) was arbitrarily defined, and all cells in the ROI were marked (cell number). Then, cell density (cells/mm2) was automatically calculated. (b) The measurement of the area of CEBCs. The inner rim of intercellular space was traced and the loop was closed. Then, the number of pixels in the loop (hatched area) was counted using Photoshop Elements 8.0 (Adobe Systems Inc., San Jose, CA, USA) after smoothing and enlarging five times by PhotoZoom Pro4 (BenVista Ltd., Houston, TX, USA). (c) The determination of the breadth of the intercellular space between neighboring CEBCs. After smoothing and enlarging by Photozoom Pro4, images were opened as jpg file in Simple PCI (Compix Inc., Cranberry Township, PA, USA). The outer and inner rims were traced carefully and the loop was closed. After 80 tracings of intercellular space for each participant, the mean breadth of each intercellular space was calculated simultaneously by breadth measurement function of Simple PCI.
