Figure 3.
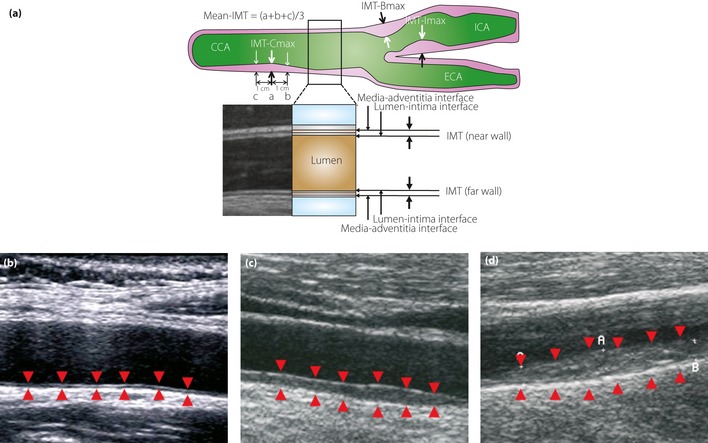
(a) The intima‐media thickness (IMT) is a double‐line pattern visualized by ultrasound on both walls of the carotid arteries. It is shown by two parallel lines that delineate the leading edges of two anatomical boundaries, the lumen‐intima and media‐adventitia interfaces. The Japan Academy of Neurosonology recommends: (i) measuring carotid IMT at the common carotid artery, carotid sinus or the bifurcation of the common carotid artery, and internal carotid artery as the thickness at the thickest point, including plaque (IMT‐Cmax, IMT‐Bmax and IMT‐Imax); (ii) recording the highest value among the three carotid IMT measurements as the maximum carotid IMT (max‐IMT); (iii) calculating the mean carotid IMT (mean‐IMT) as the mean value of the IMT values at the thickest point in the common carotid artery, and 1 cm distal and proximal from the thickest point; and (iv) handling all wall hyperplasias at a thickness of ≥1.1 mm as plaques. B‐mode views of (b) a normal carotid, (c) a carotid with moderate IMT thickening and (d) that with severe IMT thickening. Arrowheads indicate the lumen‐intima and media‐adventitia interfaces. CCA, common carotid artery; ECA, external carotid artery; ICA, internal carotid artery.
