Fig 2.
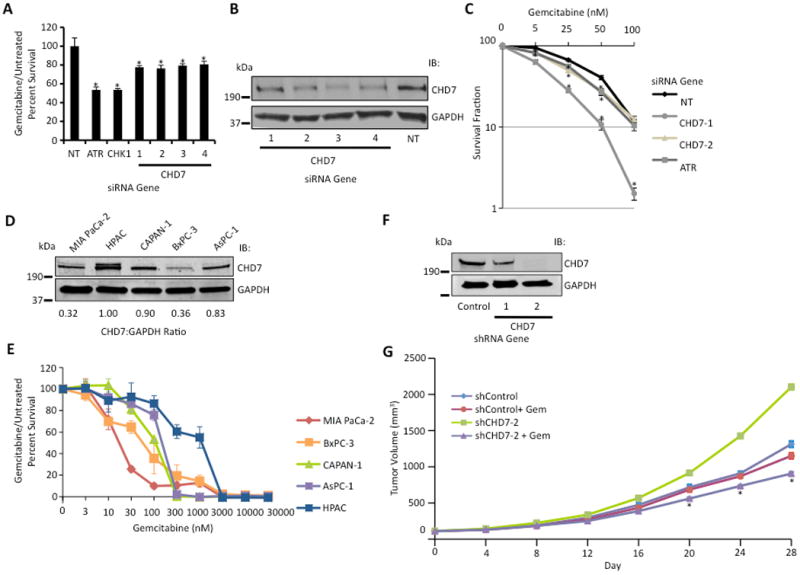
CHD7 knockdown causes gemcitabine sensitization. (A) Four siRNAs targeting CHD7 caused gemcitabine sensitization in MIA PaCa-2 cells. Treated versus untreated percent viability was calculated and the mean and standard deviation from three replicas is shown. * indicates p < 0.05. (B) Western blot analysis demonstrating efficiency of CHD7 knockdown with indicated siRNAs. (C) Clonogenic assay demonstrating gemcitabine sensitization with CHD7 silencing. MIA PaCa-2 cells transfected with siRNA against CHD7, ATR, or NT were seeded for colony formation, treated with indicated concentrations of gemcitabine for 24 hours, and assayed for surviving colonies 8-12 days later. Percent survival of colonies from treated versus untreated cells is indicated. Mean and standard deviation from three replicas are shown. * indicates p < 0.05. (D) Western blot analysis of cell lysate from MIA PaCa-2, HPAC, CAPAN-1, BxPC-3, and AsPC-1 cells with the indicated antibodies. The CHD7:GAPDH ratio of representative blot from three independent experiments is shown. (E) Gemcitabine sensitivity of MIA PaCa-2, HPAC, CAPAN-1, BxPC-3, and AsPC-1 cells following treatment with indicated concentrations of gemcitabine for 72 hours is shown. (F) Western blot analysis demonstrating efficiency of CHD7 knockdown with indicated shRNAs in MIA PaCa-2 cells. (G) Athymic nude mice with shCHD7 and shControl MIA PaCa-2 tumor xenografts were treated with or without gemcitabine (100 mg/kg) on days 0, 7, and 14, and tumor growth was measured every 4 days. Mean and standard error of mean from 6 tumors are shown. * indicates p < 0.05.
