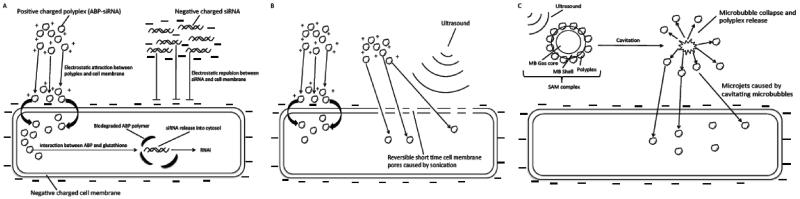
Scheme 1.
Mechanisms of intracellular siRNA delivery using arginine grafted bioreducible polymer (ABP), Ultrasound and siRNA-ABP-Microbubble (SAM) Complexes. (A) siRNA delivery using ABP or naked siRNA. Positive charged polyplexes interact with negative charged cell membrane and facilitates cellular uptake of polyplexes due to electrostatic interaction. Biodegradation of ABP polymer due to reduction of disulfide bonds in ABP backbone by intracellular glutathione leads to siRNA release into cytosol and RNAi activity. Cellular uptake of naked siRNA is declined due to repulsion of negative charge of siRNA and cell membrane. (B) siRNA delivery using ABP and ultrasound (US). Ultrasound causes short time cell membrane pores that facilitates polyplex uptake in addition to the described mechanism in (A). (C) siRNA delivery using SAM complex and ultrasound. Cavitating microbubbles (MBs) release polyplexes from microbubble shell due to interaction with US. MBs cavitation causes microjets and jetstreams that shoot polyplexes through the cell membrane in addition to the described mechanisms in (A) and (B).