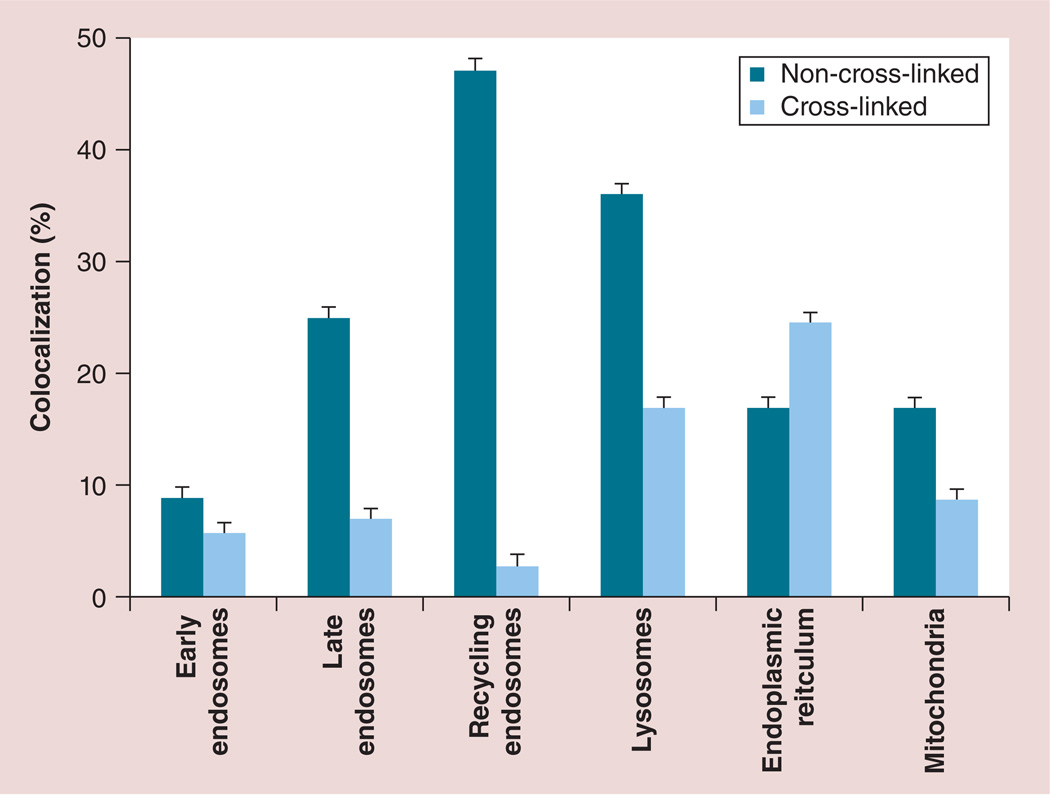
Figure 7. Effect of nanozyme cross-linking on macrophage trafficking.
Human monocyte-derived macrophages were incubated with fluorescently labeled cross-linked and non-cross-linked nanozymes for 1 h, stained with different markers to specific intracellular compartments, and a percentage of nanozyme colocalization with these markers was evaluated using confocal microscopy images. Data represent the mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 40). Stabilization of nanozyme structure by cross-linking of nanoparticles drastically altered trafficking and intracellular localization in macrophages, shifting distribution from recycling and late endosomes to endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and, in part, lysosomes. Data for non-cross-linked nanozymes were reported in [34].