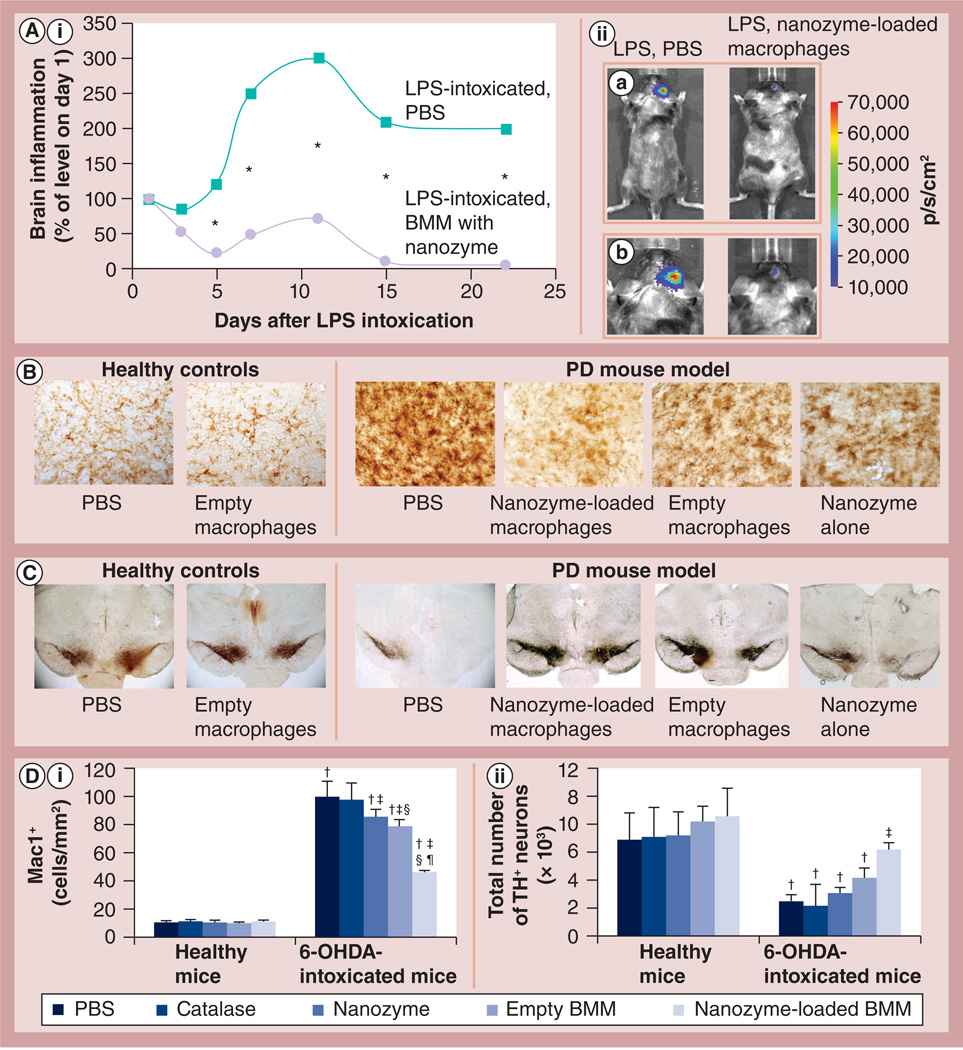
Figure 9. Effect of cross-linked nanozyme loaded into macrophages on the reduction of neuroinflammation and increase in neuronal survival in mice with brain inflammation.
(A,i)C57Bl/6 mice with LPS-induced encephalitis were injected intravenously with macrophages (5 × 106/mouse in 100 µl PBS) preloaded with cross-linked nanozyme (bis-(sulfosuccinimidyl)suberate sodium salt, charge ratio = 6; 2 mg/ml catalase) or PBS. (A,ii) Image visualization and infrared spectroscopy images over 20 days were taken 10 min after intraperitoneal injection of a XenoLight™ RediJect probe (Caliper LifeSciences, MA, USA). (A,ii,a) Whole body images and (A,ii,b) images of the mouse head for the corresponding time. The chemiluminescent signal was quantified and presented as radiance ratios of treated animal versus 24 h after LPS injection at various times. Macrophages preloaded with the cross-linked nanozyme caused prolonged decreases of neuroinflammation in LPS-intoxicated mice. Data represent mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 5). The statistical significance of inflammation levels compared with control LPS-intoxicated mice is shown by asterisk: *p < 0.05. (B–D) C57Bl/6 mice were intracranial injected with 6-OHDA. A total of 48 h later, animals were intravenously injected with macrophages preloaded with catalase alone, cross-linked nanozyme alone, empty macrophages or macrophages preloaded with cross-linked nanozyme, and 5 weeks later they were sacrificed and midbrain slides were stained for expression of (B) Mac1+, a marker for activated microglia or (C) tyrosine hydroxylase, a marker for dopaminergic neurons. (D) Quantification of microglial activation and neuronal survival. Values represent mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 6), and p < 0.05 compared with †: PBS (healthy controls); †: 6-ODHA (PD mouse model); §: catalase alone (in 6-OHDA intoxicated mice); and ¶: empty macrophages (in 6-OHDA-intoxicated mice). Selected images of several additional control groups are presented on Supplementary Figure S9. Whereas 6-OHDA treatment caused significant microglia activation and neuronal loss, administration of nanozyme-preloaded macrophages significantly decreased oxidative stress and increased neuronal survival. The administration of empty M2 macrophages slightly decreased microglia activation, and increased the number of dopaminergic neurons in mice with brain inflammation. 6-OHDA: 6-Hydroxydopamine; BMM: Bone marrow-derived macrophage; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; PBS: Phosphate-buffered saline; PD: Parkinson’s disease