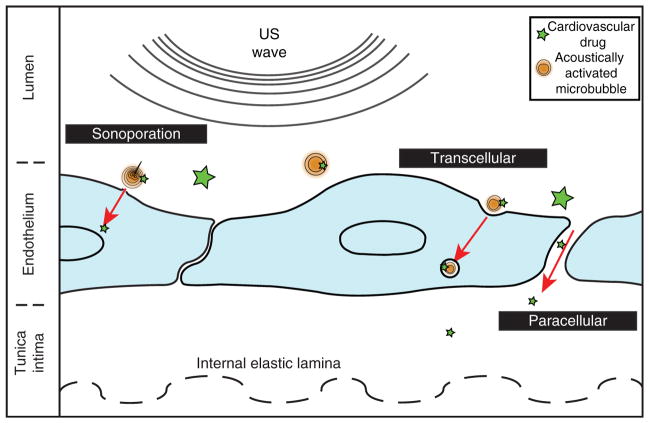
Figure 1. An overview of three penetration routes stimulated for ultrasound-mediated drug delivery.
Sonoporation refers to the localized, mechanical disruption of a plasma membrane, which allows drugs and ions to diffuse passively. Transcellular pathways, such as endocytosis, involve active transport of drug via cytosolic vesicles. The paracellular route occurs when endothelial cells spread apart, either due to desquamation or by tight junction breakdown from bubble-induced shear stress.