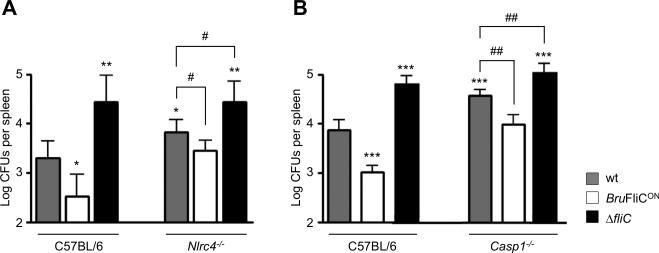
Fig. 7. NLRC4 inflammasome is implicated in the control of B. melitensis infection in vivo.
Wild type, Nlrc4-/- (A) and Casp1-/- (B) C57BL/6 mice (n=5) were injected i.p. with 4 × 104 CFUs of B. melitensis wt, BruFliCON or ΔfliC strain, as indicated in the figure. Mice were sacrificed 21 days post-infection and CFUs per spleen were determined. These results are representative of at least two independent experiments. Data have been analysed by ANOVA I after testing the homogeneity of variance (Bartlett). * ,** and *** denote significant (p<0.05, p<0.01 and p<0.001 respectively) differences in relation to C57BL/6 wt infection by wt bacteria. # and ## denote significant (p<0.05 and p<0.01 respectively) differences in relation to knock-out mice infection by wt bacteria.