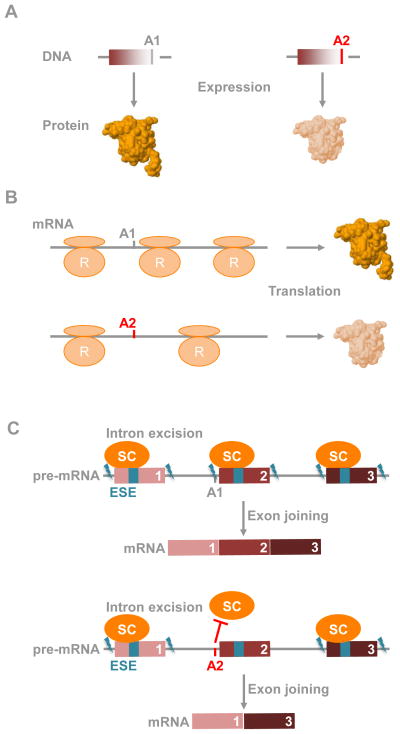
Figure 1. Genetic risk-variants mapping to coding regions.
A. Non-synonymous genetic risk-variants alter structure and activity of encoded proteins. A1 and A2 are the two alleles of a genetic risk variant. In all figures, A1 is the normal allele (or risk allele), and A2 is the risk allele (or normal allele).
B. Synonymous genetic risk-variants alter translational rate, further influencing protein folding. R: Ribosome.
C. Genetic risk-variants disrupt exonic splicing enhancers (ESE), further leading to exon skipping. SC: splicing complex.