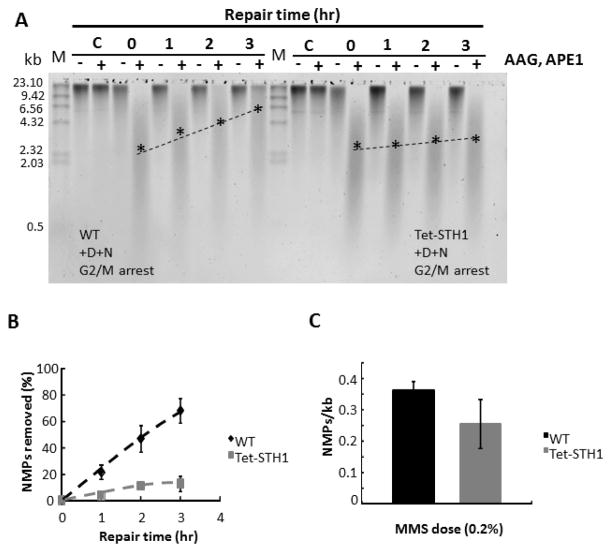
Figure 2. A,B,C. Depletion of RSC complex in Tet-STH1 strain dramatically inhibits BER genome-wide.
The Tet-STH1 and WT strains were grown in the presence of doxocycline for 20 hours, arrested at G2/M phase with nocodazole and treated with MMS. Cells were maintained at G2/M through the repair time course. For each time point cell aliquots were collected and genomic DNA was purified. Genomic DNA was processed with (+) or without (−) enzymatic cocktail composed of glycosylase (AAG) and endonuclease (APE1). Enzymes convert methylated purines to single strand breaks. Single strand breaks were separated on the alkaline gel and DNA was visualized with SYBR gold staining. A. A representative gel showing repair time course in WT and STH1- depleted Tet-STH1 strains. M: marker DNA size standard (λ/HindIII); C: untreated cells; 0: cells damaged with MMS; 1–3: repair time course in hours. Positions of the approximate median migration distance of the fragments in each lane are shown with asterisks (*) and are connected by a dotted line. B. Repair time course of N-methylpurines (NMPs). Data represent mean ± 1 s.d. from three independent experiments. C. Formation of NMPs in the genomes of WT and STH1- depleted cells. STH1- depleted and G2/M synchronized cells were damaged with MMS. Genomic DNA was purified and number of NMPs was analysed as described in materials and methods. Data represent mean ± 1 s.d. from three independent experiments.