Figure 1.
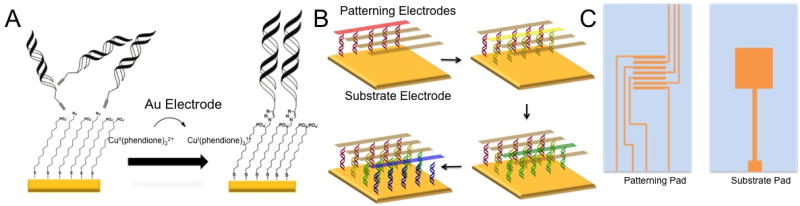
Selective activation for specific covalent attachment of DNA to particular locations. (A) An inert Cu(II) catalyst is electrochemically activated to an active Cu(I) species capable of catalyzing the [3+2] azide-alkyne cycloaddition between alkyne-modified DNA and an azide-terminated thiol monolayer. (B) Four different sequences of DNA are patterned onto a single substrate pad through sequential catalyst activations. (C) Design for patterning electrodes and substrate electrode. The patterning pad (left) contains four working electrodes that are individually addressable interspersed with three reference electrodes. The substrate pad (right) contains a single, large gold pad and a working electrode contact to the pad.
