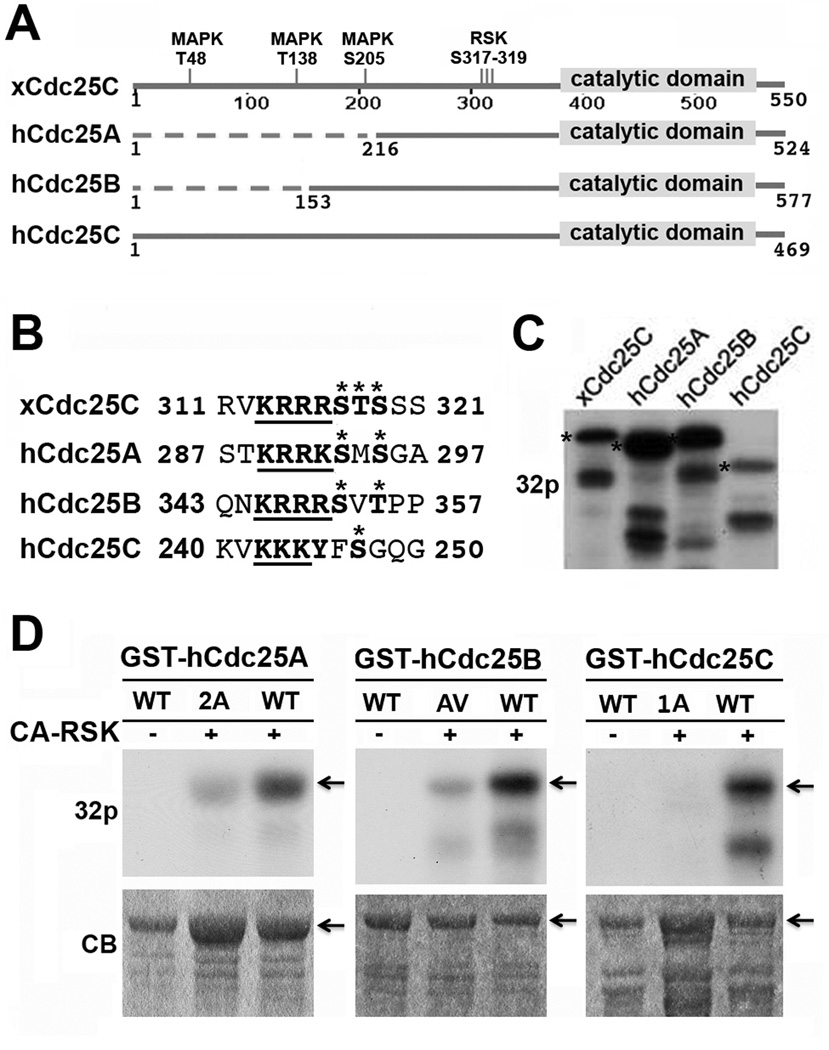
Figure 1. CA-RSK phosphorylates recombinant hCdc25 isoforms at a conserved motif near the catalytic domain.
(A) Sequence alignment of hCdc25A, B, and C with xCdc25C. Conserved and non-conserved regions are schematically illustrated as solid and dotted lines, respectively. (B) Sequence alignment of the region of xCdc25C containing the three RSK2 phosphorylation sites (317–319) with hCdc25A, B, and C. Asterisks indicate the RSK2 phosphorylation sites in xCdc25C and the putative phosphorylation sties in hCdc25 isoforms. The underlined bold types indicate the string of basic residues on the N-terminal side of the potential RSK phosphorylation sites. (C) GST-tagged xCdc25C, hCdc25A, hCdc25B or hCdc25C was incubated at room temperature for 30 min with CA-RSK in the presence of γ-32P-ATP. The products were separated by SDS-PAGE and subjected to autoradiography. Stars indicate full-length proteins. (D) The immobilized wild type (WT) and indicated mutant form of GST-hCdc25A, GST-hCdc25B or GST-hCdc25C were incubated with CA-RSK in the presence of γ-32P-ATP for 30 min at room temperature. Proteins eluted from washed beads were separated by SDS-PAGE and subjected to autoradiography. Arrows indicate full-length proteins.