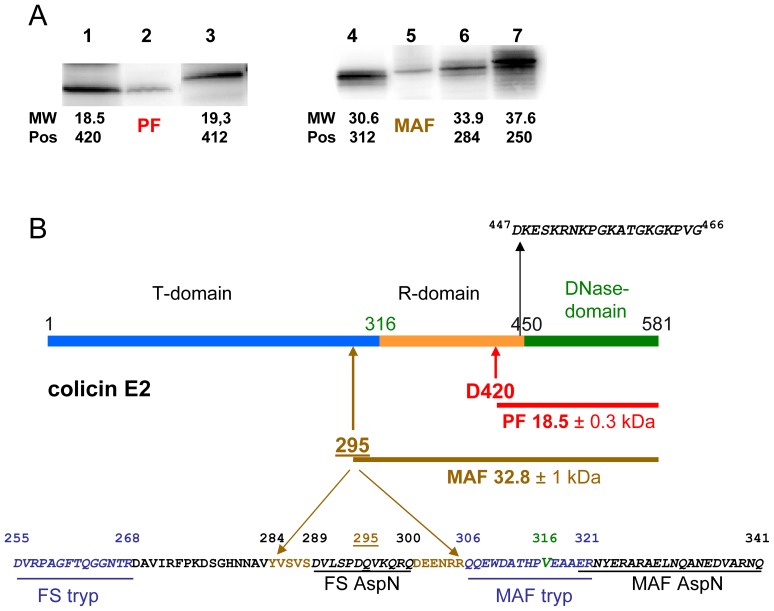
Figure 3. Identification of in vivo cleavage products of colicin E2.
(A) Comparison of the migration of the in vivo processed (lane 2, PF) and the membrane attached (lane 5, MAF) colicin-E2 forms with various C-terminal peptides of colicin E2, synthesized in vitro by a coupled transcription-translation Zubay-30S system. Peptides Asp420-Lys581 (lane 1, 18.5 kDa), Asp412-Lys581 (lane 3, 19.3 kDa), Ala312-Lys581 (lane 4, 30.6 kDa), Tyr284-Lys581 (lane 6, 33.9 kDa) and Asn250-Lys581 (lane 7, 37.6 kDa) were separated on 15% SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting with anti-colicin E2 antiserum. (B) The domain structure of colicin E2 is given. Peptide sequence around the junction of the T- and R-domains of colicin E2 (at position V316; indicated in green) is shown. The sequence of the most N-terminal peptide (between positions 447–466) detected in the PF by mass spectrometry (MS) is shown and both the deduced processing site, at or close to residue D420, and size of the PF are indicated. The approximate location of the N-terminal residue of MAF is between positions 284 and 306 (indicated at position 295+/−10 amino acids), as estimated from the migration (A) and mass spectrometric analysis of both the full-size colicin E2 and the colicin E2 MAF, shown at the bottom. Peptides (underlined amino acids in italics) recovered from MS analysis after trypsin (tryp; shown in blue) or AspN (shown in black) treatment are delineated. Peptides, only recovered from the full-size colicin E2 molecule are labelled FS while those recovered from both MAF and FS are labelled as MAF.