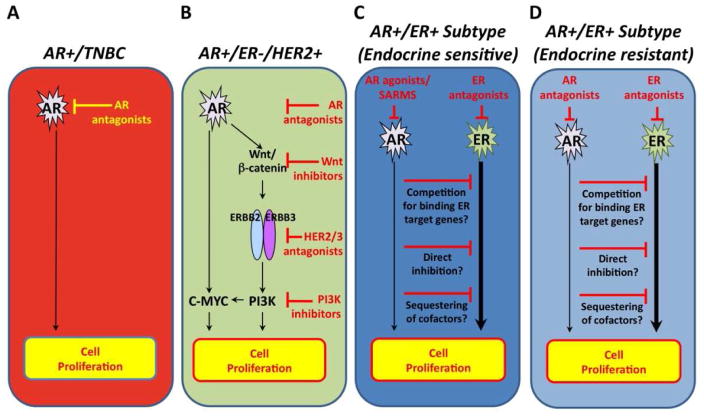
Figure 1. Preclinical insights of AR signaling according to breast cancer subtype.
AR antagonists have been shown to inhibit cell proliferation in A) TNBC AR+ and B) ER-HER2+AR+ breast cancer subtypes, the latter through its interaction with the HER2/3, Wnt/β-Catenin and c-MYC pathways. On the other hand, AR antagonists results in increased cell proliferation in C) ER+AR+ breast cancer cells through its interaction with the ER signaling pathway, and AR agonists may therefore be of benefit in this setting. D) AR overexpression may be a mechanism of Tamoxifen resistance, and inhibition of AR may be of benefit in this setting.