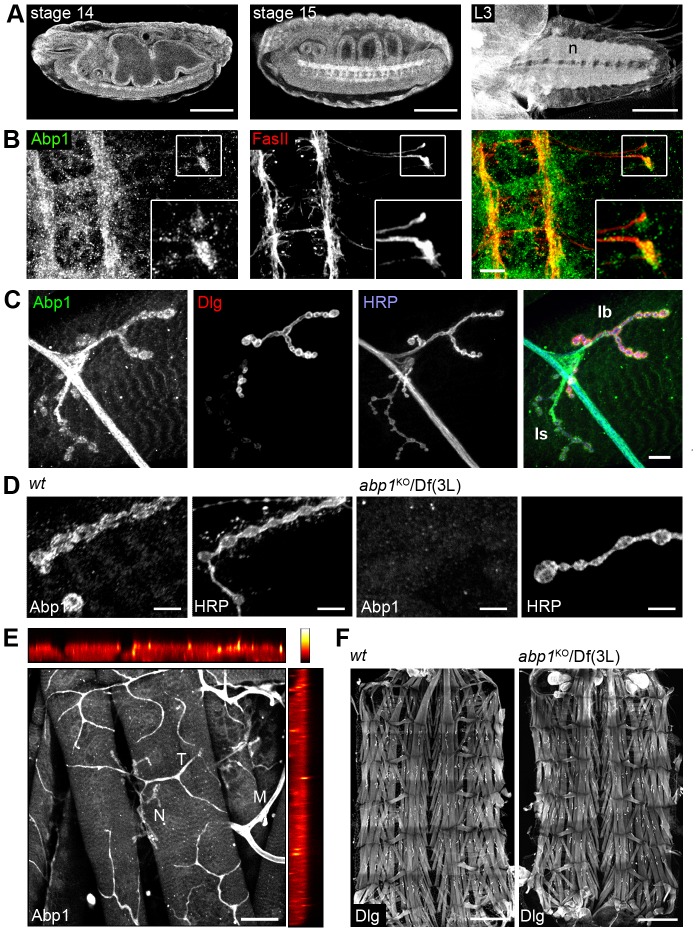
Figure 2. Abp1 is highly expressed in the central nervous system.
(A) Immunolabeling of endogenous Abp1 at indicated stages of development. Left, confocal lateral view of stage 14 embryo; middle, confocal, ventro-lateral view of stage 15 embryo; right, confocal image of a 3rd instar larval brain. Embryos display strong Abp1 immunoreactivity in epithelia and the CNS (left), in the commissures and longitudinal tracks of the CNS (middle) as well as in the neuropil (n) of the ventral nerve cord of 3rd instar larvae. Bars, 100 µm. (B) Maximum projections of a confocal stack of a stage 15 embryo immunostained with anti-Abp1 antibodies showing that besides in the commissures and longitudinal tracks of the CNS Abp1 is present in motoneuronal growth cones marked with anti-FasII antibodies. Boxed area is presented as enlarged inset. Bar, 10 µm. (C) Abp1 immunoreactivity at NMJs of a 3rd instar larvae costained with postsynaptic (Dlg) and presynaptic markers (HRP). Note that in contrast to Dlg labeling, Abp1 immunoreactivity is nearly equally strong at type Ib and type Is synaptic boutons. Bar, 10 µm. (D) Anti-Abp1 immunostaining of wt versus abp1KO/Df(3 L) NMJs showing that the anti-Abp1 immunosignal at NMJs is specific. Bar, 10 µm. (E) Overview of anti-Abp1 immunostaining at muscles 6/7 NMJs of a 3rd instar larvae (maximum projections of confocal stack). Note that besides a low expression in muscles, Abp1 is enriched in tracheae (example marked with T), axons of motoneurons (example marked with M) and NMJs (example marked by N). Colored panels at top and right display the intensity of the anti-Abp1 signal in Z-direction in pseudo colors encoding for the fluorescence intensity (see scale at upper right). Bar, 50 µm. (F) Maximum projections of stitched confocal images of anti-Dlg-stained body wall preparations show normal segmentation, muscle organization and innervations of an wt (left) and an abp1 KO/Df(3 L) fly (right). Bar, 500 µm.