Figure 3.
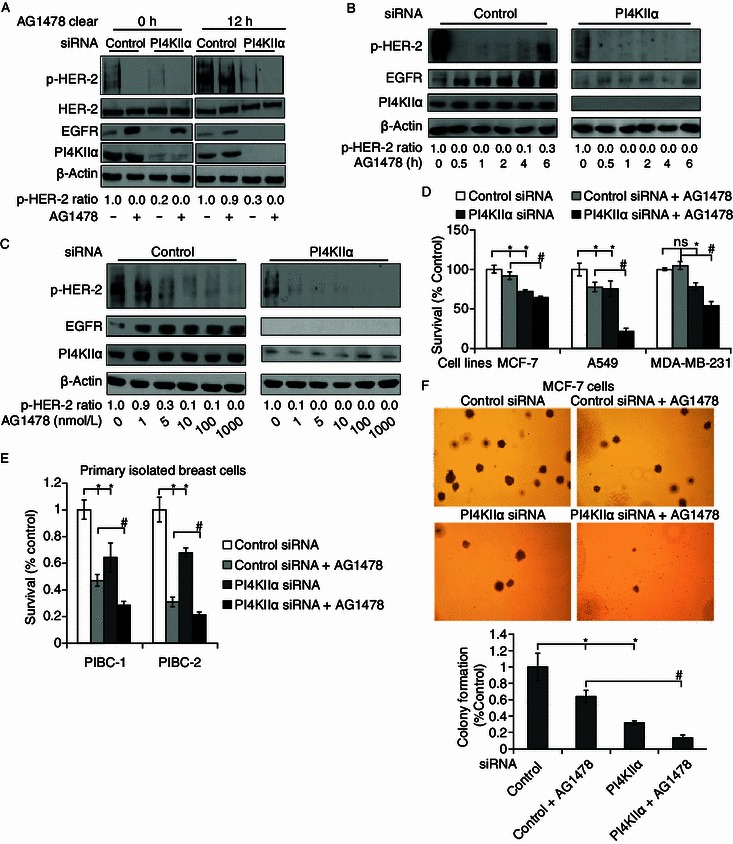
Ehanced effects of PI4KIIα knockdown and EGFR inhibition by AG1478 on HER-2 activity and cell viability. (A–C) Time and dose effect of AG1478 on p-HER-2 in PI4KIIα siRNA-treated cells and controls. MCF-7 cells were transfected with control or PI4KIIα siRNA before the following treatments (A–C), EGF was added for 10 min, lysed the cells and analyzed the levels of phosphorylated HER-2, the expression levels of EGFR and PI4KIIα by Western blot, with β-actin as the loading control. (A) 100 nmol/L AG1478 was added into the cell medium for 2 h except for controls, and then removed by washing cells for three times using PBS, cells were lysed or cultured as indicated for another 12 h. (B) Cells were incubated with 100 nmol/L AG1478 for indicated times. (C) Cells were treated with different concentrations of AG1478 for 2 h. (D) Effect of PI4KIIα knockdown and AG1478 (5 μmol/L) on cell viability of MCF-7 cells, A549 cells and MDA-MB-231 cells. (E) Effect of PI4KIIα suppression and AG1478 on cell viability of two primary isolated breast cancer cells. Primary cell lines PIBC1 and PIBC2 were transfected with control or PI4KIIα siRNA for 24 h, and then treated with 5 μmol/L AG1478 for another 48 h, except controls. (F) Effect of PI4KIIα suppression and AG1478 on colony formation in MCF-7 cells. Anchorage-independent cell growth was measured using a soft agar assay. Colony numbers were determined after 14 days incubation in soft agar. Data are presented as mean ± SD, *P < 0.01, as compared to control RNAi cells, while #P < 0.01, as compared to cells treated with both AG1478 and control RNAi. All results presented above represent data from three independent experiments
