Figure 2.
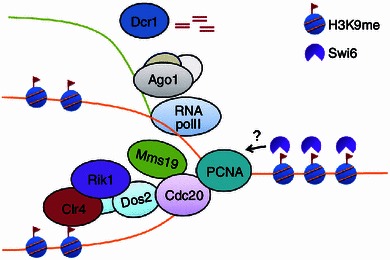
Model of inheritance of H3K9 methylation during DNA replication. During S phase of the cell cycle, Cdc20, the catalytic subunit of Pol ε, travels with the replication fork to synthesize the leading strand DNA. When it reaches heterochromatin, Cdc20 may sense the epigenetic state of parental nucleosomes by interacting, directly or indirectly, with the epigenetic reader protein, Swi6/HP1, associated with parental histones. This leads to recruitment of the ClrC complex to replication forks. Histone modification enzymes in the ClrC complex, including Clr4 and Lid2, modify the histones on daughter DNA to ensure hypermethylation of H3K9. Meanwhile, Cdc20 recruits the transcription regulator, Mms19, to heterochromatin, which in turn promotes heterochromatin transcription by RNA Pol II. These transcripts are processed by RNAi machinery into siRNAs, which facilitate the formation of heterochromatin after replication
