Figure 4. B-cell depletion.
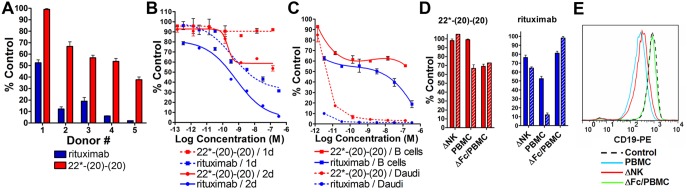
Freshly isolated PBMCs were incubated for two days with 22*-(20)-(20) (red) or rituximab (blue) prior to counting the viable B cells The relative viable B cell count is expressed as % Control, which was derived by dividing the specific B cell count by that measured following treatment with the control mAb (labetuzumab). Error bars, Std. Dev. (A) B-cell depletion with 140 nM rituximab or 22*-(20)-(20) in PBMCs from 6 unique donors. (B) B-cell depletion at 24 h and 48 h with antibody titrations using PBMCs from Donor 4. (C) Daudi Burkitt lymphoma cells were spiked in PBMCs from Donor 3 and treated with titrations of the antibodies. Daudi and normal B cells were separated by forward scattering and counted independently. (D) 140 nM of 22*-(20)-(20) (left, red) or rituximab (right, blue) were incubated with NK-depleted (ΔNK) or intact PBMCs, which were alternatively treated with Fc-deleted fragments (ΔFc/PBMC) of each antibody. Donor 1, solid bar; Donor 2, hatched bar. (E) Reduction of CD19 on B cells by trogocytosis. Control was PBMCs treated with labetuzumab (black dashed trace). Fc-deleted 22*-(20)-(20) was incubated with PBMCs (green trace). Intact 22*-(20)-(20) was incubated with PBMCs (blue trace) or NK cell-depleted PBMCs (red trace). Histograms show the fluorescence intensity for anti-CD19-PE.
