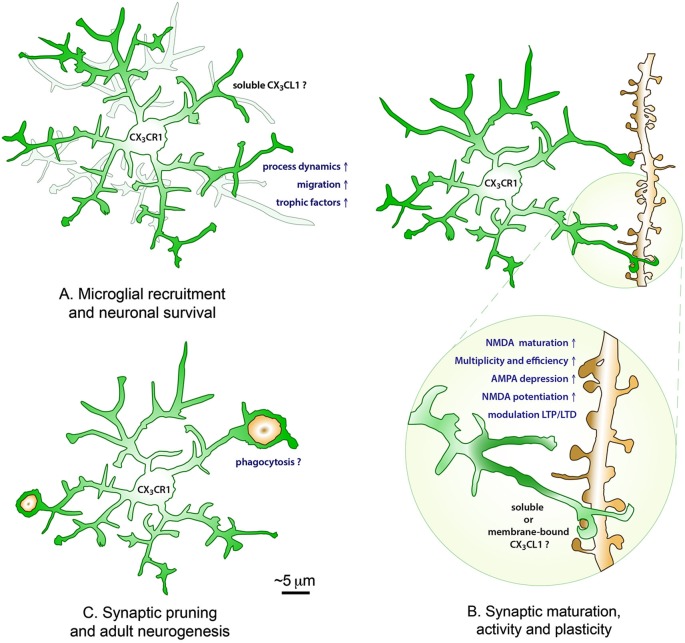
Figure 1.
The roles of CX3CL1-CX3CR1 interactions in the healthy brain. During postnatal development, fractalkine signaling is promoting microglial recruitment to neuronal circuits by increasing their process dynamics and cellular migration, as well as modulating neuronal survival via the release of trophic factors (A). During postnatal development and adulthood, soluble and/or membrane-bound fractalkine further contribute to the maturation, activity and plasticity of excitatory synapses by promoting the maturation of NMDA receptors (transition from GluN2B to GluN2A subunits), the multiplicity and efficiency of synaptic transmission, the depression of AMPA receptors and potentiation of NMDA receptors, and the modulation of LTP and LTD at the Schaffer collateral synapse in the hippocampus CA1 (B), with lasting consequences on the brain functional connectivity, learning and memory, and the behavioral outcome. Additionally, fractalkine signaling might be influencing the developmental pruning of synapses and adult hippocampal neurogenesis by regulating microglial phagocytosis of synaptic elements and newborn apoptotic cells during normal physiological conditions (C).