Figure 2.
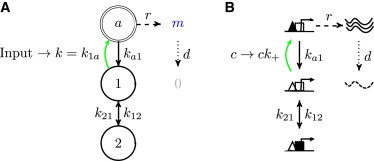
Promoters as state transition graphs. (A) A state transition graph for an example three-state promoter. Active state a (double circle) expresses mRNA m at rate r, which are then degraded with rate d. Transition into a (green arrow) is affected by the input that modulates rate . Stochastic transitions between promoter states are an important contribution to the noise, . (B) A possible mechanistic interpretation of the diagram in (A): state 1 is an unoccupied promoter, state 2 is an inaccessible promoter (occupied by a nucleosome or repressor, solid square). Transition to the active state (green arrow) is modulated by changing the concentration c of activators (solid triangles) that bind their cognate site (open triangles) at the promoter with the rate . To see this figure in color, go online.
