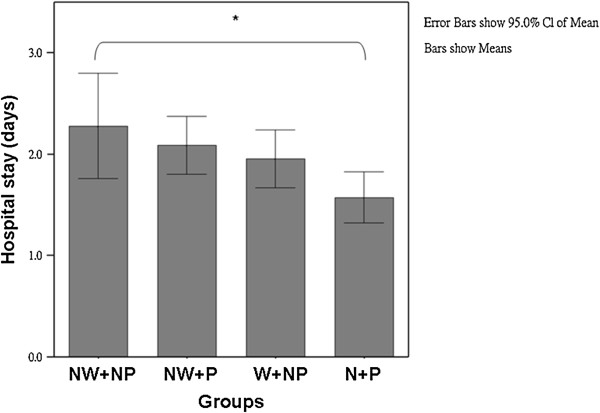
Figure 2.
The duration of the hospital stay of the 4 groups of patients [i.e., patients who received a local anesthetic at the end of laparoscopic cholecystectomy either with an intraperitoneal local anesthetic (W + P group; n = 55) or without an intraperitoneal local anesthetic (W + NP group; n = 55), and patients who received no local wound anesthetic at the end of LC either with an intraperitoneal local anesthetic (NW + P group; n = 55) or without an intraperitoneal local anesthetic (NW + NP group; n = 55)]. *p < 0.05. The W + P patients had significantly shorter hospital stays than the NW + NP patients. All data are presented as the mean with 95% confidence interval standard deviations. NW + NP = no wound anesthetic and no intraperitoneal anesthetic use; NW + P = no wound anesthetic but intraperitoneal anesthetic use; W + NP = wound anesthetic but no anesthetic use; W + P = wound anesthetic and intraperitoneal anesthetic use.