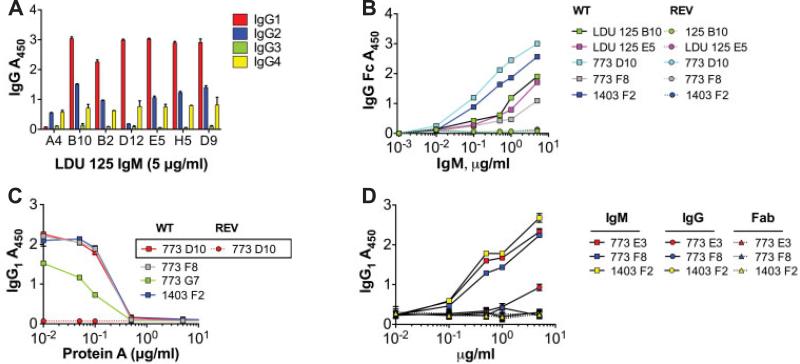
Figure 4.
The modestly hypermutated VH1-69+/Vκ3-20+ IgM from patients with hepatitis C virus are rheumatoid factors. A, Monoclonal antibodies (mAb) from subject LDU 125 were expressed as IgM, and serial dilutions were incubated on enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) plates coated with IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, or IgG4 and were detected with anti-IgM. Binding was strongest for IgG1 followed by IgG2 and IgG4, and was weakest for IgG3. B, Serial dilutions were incubated as in A, except ELISA plates were coated with IgG Fc. The results demonstrated that IgM bound to the Fc portion of IgG. C, Before incubation with IgG1-coated plates, IgM (1 μg/ml) were incubated with serial dilutions of protein A. For all clones tested, preincubation with 0.5–1 μg/ml protein A yielded 50% inhibition of binding. D, Anti-IgG1 activities of Ig expressed as either IgM, IgG, or Fab were compared. These VH1-69+/Vκ3-20+ mAb bound IgG1 when expressed as IgM, but not as IgG or Fab, indicating that the binding to IgG1 is of low affinity and depends upon the avidity conferred by multimeric IgM. Values are the mean ± SD. WT = wild type; REV = germline reverted.