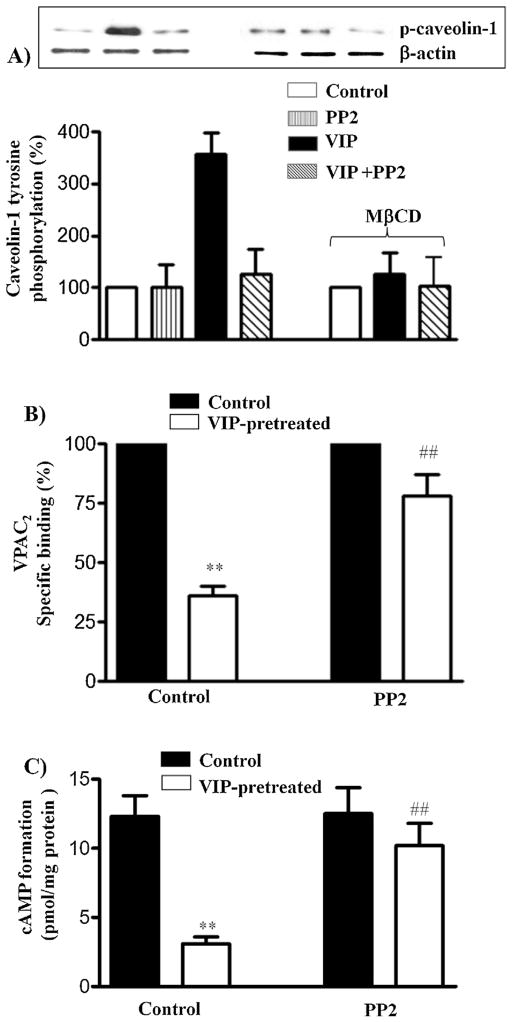
Fig. 3.
Tyrosine phosphorylation of caveolin-1 and the effect of Src kinase inhibitor PP2 on VPAC2 receptor internalization and desensitization. (A) Control muscle cells and cells treated with MβCD were treated with VIP (1 μM) for 10 min in the presence or absence of Src kinase inhibitor PP2 (1 μM). Control cells were also treated with PP2 in the absence of VIP. Tyrosine phosphorylation of caveolin-1 was examined in caveolin-1 immunoprecipitates using phospho-specific antibody by western blot analysis. (B) Control muscle cells were treated with VIP (1 μM) for 30 min in the presence or absence of Src kinase inhibitor PP2 (1 μM) and 125I-VIP binding to surface receptors was measured. VPAC2 receptor internalization was assessed by the decrease in 125I-VIP binding to surface receptors after pretreatment with VIP. Results are expressed as percent of control specific binding in the absence of pretreatment and the specific binding was similar in control cells and in cells treated with PP2. Internalization of VPAC2 receptors, however, was significantly attenuated in cells treated with PP2. Values are expressed as means ± SE of 4 experiments. **p < 0.01 significant inhibition of specific binding compared to control cells. ##p < 0.01 significant attenuation of internalization in the presence of PP2 compared to cells in the absence of PP2. (C) Adenylyl cyclase activity in response to VIP was measured as increase in cAMP formation in control cells and after treatment of the cells with VIP for 30 min in the presence or absence of PP2 before VIP-induced increase in cAMP formation was measured by radioimmunoassay. Desensitization of VPAC2 receptors was assessed by the decrease in cAMP response after pretreatment with VIP. Results are expressed as percent of control response to VIP before pretreatment. Basal levels (2.1 ± 0.3 to 2.4 ± 0.2 pmol/mg protein) were not significantly different in control cells and in cells treated with PP2. Pretreatment of cell with VIP inhibited cAMP formation (desensitization) in response to subsequent addition of VIP (1 μM). Desensitization of VPAC2 receptors, however, was significantly attenuated in cells treated with PP2. Results are expressed as pmol/mg protein above basal levels. Values are expressed as means ± SE of 4 experiments. **p < 0.01 significant inhibition of cAMP formation compared to control cells. ##p < 0.01 significant attenuation of desensitization in the presence of PP2.