Figure 1.
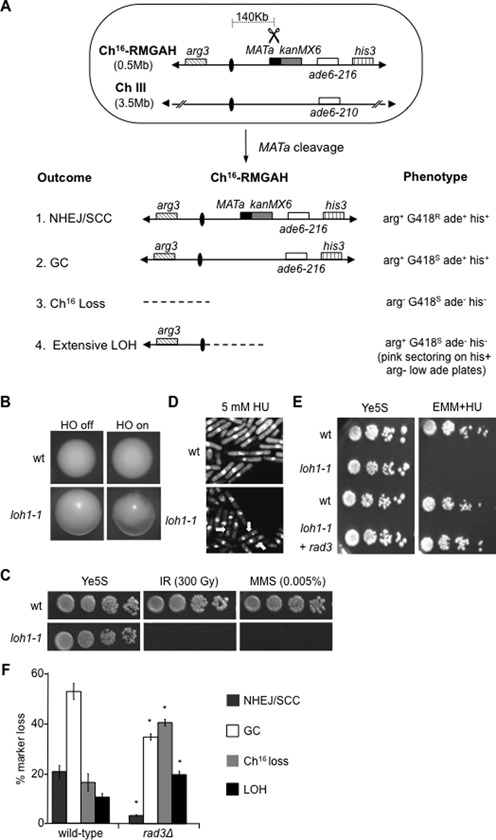
Rad3ATR suppresses break-induced extensive LOH. (A) Schematic of the minichromosome Ch16-RMGAH. The relative positions of the arg3 marker (diagonal stripes), centromeres (ovals), the MATa site (black), the kanMX6 resistance marker (gray), the complementary ade6 heteroalleles (ade6-M216 and ade6-M210; white) and the his3 marker (vertical stripes) on Ch16-RMGAH and ChIII are shown as described previously (35). The sizes of the ChIII and Ch16 are shown. In Ch16-RMYAH, kanMX6 is replaced by hph. Derepression of pREP81X-HO (not shown) generates a DSB at the MATa target site (scissors). Possible outcomes resulting from DSB induction, together with schematics of the minichromosome, and expected phenotypes are shown. (B) Colony sectoring of wild-type or loh1–1 arg+ G418S ade− his− colonies grown on Edinburgh minimal medium (EMM) plus uracil, histidine and low adenine (5 mg/l) without arginine (arg- plates) thus facilitating detection of extensive LOH (LOH) in the presence (HO off) or absence (HO on) of thiamine. (C) Ten-fold serial dilutions of wild-type (WT) Ch16-RMGAH (TH2130) or loh1–1 (TH4089) strains on Ye5S plates, Ye5S plates exposed to 300 Gy IR, or 0.005% MMS as indicated. (D) 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) stained wild-type Ch16-RMGAH (TH2130) or loh1–1 (TH4089) strains either untreated or following exposure to 5 mM HU for 6 h. ‘Cut’ phenotypes indicated (yellow arrows). (E) Serial dilutions of wild-type Ch16-RMGAH (TH2130), loh1–1 (TH4089) with pREP41X empty vector or pREP41X-rad3 (TH4093) on Ye5S and 10 mM HU EMM plates without thiamine, to derepress pREP41X expression. (F) Percentage DSB-induced marker loss of Ch16-RMGAH in wild-type (TH2130) and rad3Δ (TH2941) backgrounds. The levels of NHEJ/sister chromatid conversion (SCC), GC, Ch16 loss and extensive LOH are shown. Data are the mean of three experiments and standard errors of the mean are indicated. The asterisk (*) represents significant difference compared to wild-type.
