Figure 1.
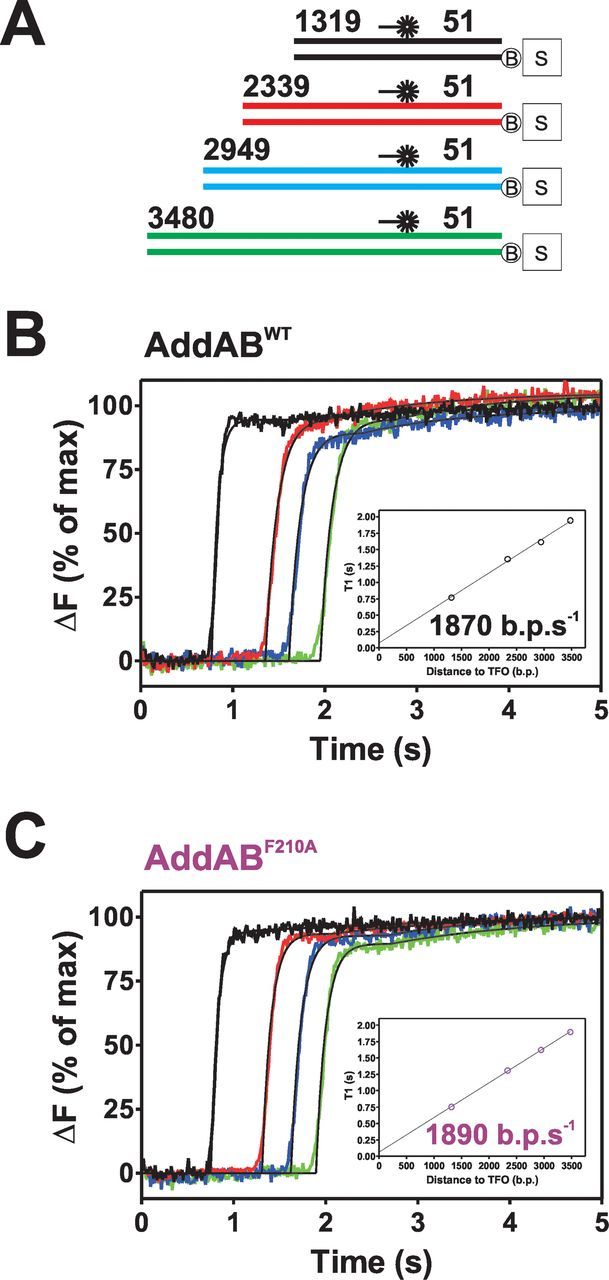
AddABF210A translocates normally on Chi-free DNA. (A) Schematic of substrates used for triplex displacement experiments; the colours used match the displacement curves shown in B and C. (B) Triplex displacement by wild-type (WT) AddAB. 2 nM DNA molecules were prebound by 10 nM AddAB enzymes. Reactions were initiated by mixing with an equal volume of ATP (1 mM) and AddAK36AB (200 nM) at 37°C. Data are the average of at least three transients and normalized to the endpoint of fluorescence. (C) Triplex displacement by AddABF210A using the same conditions as (A). Data are the average of at least three transients and normalized to the fluorescence endpoint. Insets show T1 lag times obtained from a fit to data in (A and C) using Equation (1). These values are plotted against the distance to the TFO and fit to a linear function (black lines), the gradient of which equates to the translocation rate.
