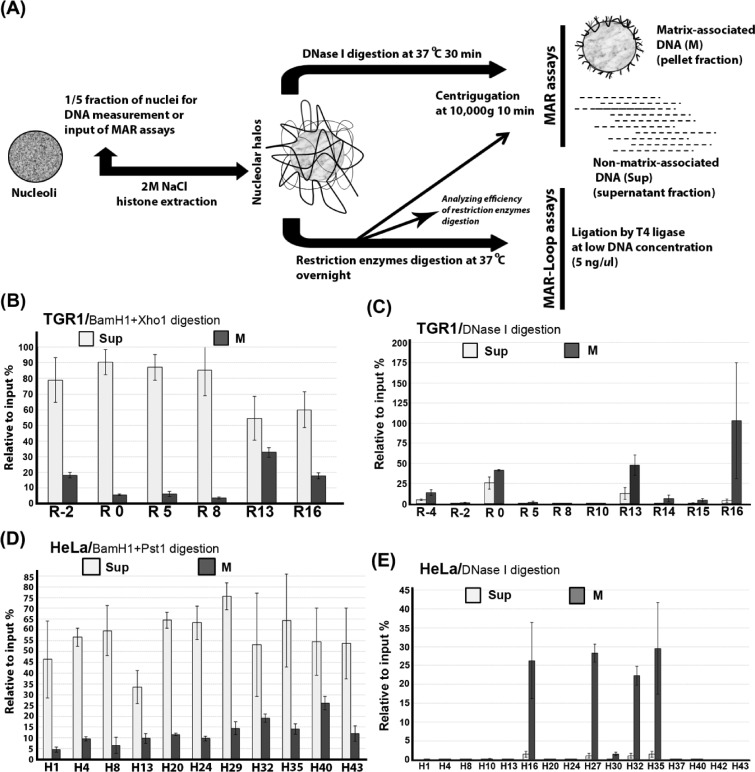
Figure 2.
Preferential matrix attachment of rDNA genes via the intergenic spacer (IGS) region. (A) Diagram showing the procedure used for isolation of nucleolar halos and the preparation of nucleolar matrix and subsequent MAR and MAR-loop assays. (B) Preferential attachment of rDNA genes to nuclear matrix via IGS sequences in growing TGR-1 cells. The relative association of different regions of the rDNA repeat to nucleolar matrix (M) after digestion with BamH1 and Xho1 as well as the levels of released non-matrix associated regions (Sup) are shown. (C) Fine mapping of nucleolar-matrix-associated rDNA fragments after DNase I treatment of nucleolar matrix from growing TGR-1 cells. (D) Preferential attachment of rDNA genes to nuclear matrix via sequences throughout the IGS region in growing HeLA cells. The supernatant fraction and pellet fraction are separated after restriction enzymes (BamH1+Pst1) digestion. (E) Fine mapping of nucleolar-matrix-associated rDNA fragments after DNase I treatment of nucleolar matrix from growing HeLa cells. The values plotted in (B–E) are the means and standard deviation of results from three independent experiments.