Figure 4.
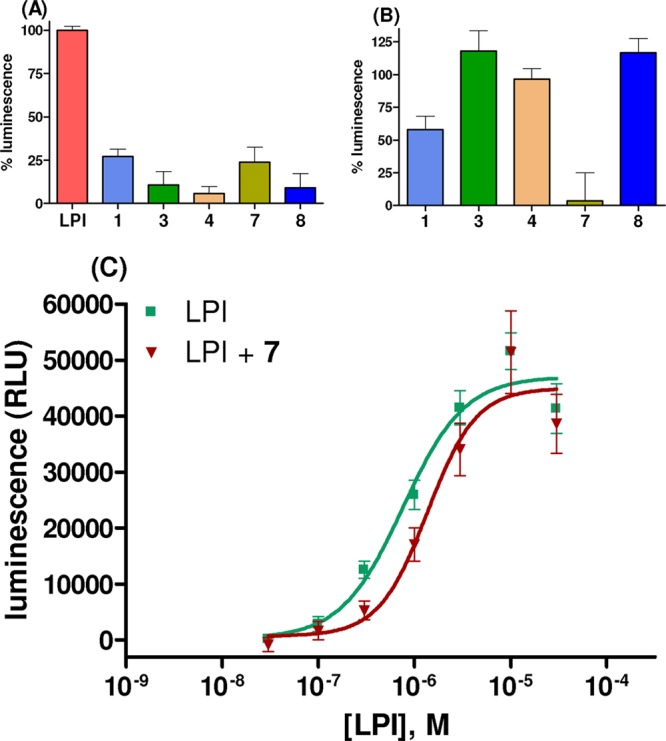
(A) Effects of LPI (GPR55 agonist, 1 μM), honokiol (1), magnolol (3), 8,9-dihydroxydihydromagnolol (4), tetrahydromagnolol (7), and trans-isomagnolol (8) (10 μM each) on β-arrestin recruitment to human GPR55 receptors recombinantly expressed in CHO cells. (B) Inhibition of LPI (1 μM)-induced β-arrestin recruitment to human GPR55 by 1, 3, 4, 7, and 8 (10 μM). The results in A and B represent means ± SEMs of three independent experiments performed in duplicates. Data are expressed as the percent luminescence related to the effect of LPI (1 μM; ≥50% of maximal effect; EC50 = 0.769 μM) set at 100%. (C) Concentration-dependent effect of LPI on β-arrestin recruitment to human GPR55 receptors recombinantly expressed in CHO cells in the absence and in the presence of tetrahydromagnolol (7, 10 μM). Data points are means ± SEMs of three independent experiments, performed in duplicates. A KB value of 13.3 ± 2.0 μM was determined for tetrahydromagnolol; RLU = relative luminescence units. Recruitment of β-arrestin to the receptor was detected by measuring luminescence emission, based on a β-galactosidase enzyme fragment complementation assay (DiscoverX).
