| Title: | Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Receptor Inhibitors | ||
| Patent Application Number: | WO 2012/145471 A1 | Publication Date: | 26 October 2012 |
| Priority Application: | US 61/477,937 | Priority Date: | 21 April 2011 |
| Inventors: | Balachandran, S.; Dinsmore, C. J.; Roychowdhury, A.; Sharma, R.; Vishwakarma, R. A. | ||
| Assignee Company: | Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.; 126 East Lincoln Avenue, Rahway, New Jersey 07065-0907, United States | ||
| Piramal Healthcare Ltd.; Piramal Tower, Ganpatrao Kadam Marg, Lower Parel, Mumbai 400013, India | |||
| Disease Area: | Cancer | Biological Target: | insulin-like-growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1 R) and insulin receptor (IR) |
| Summary: | The invention in this patent application relates to sulfonyl indole derivatives represented by Formula (I) that are capable of inhibiting, modulating, and/or regulating Insulin-Like-Growth Factor 1 Receptor (IGF-1 R) and Insulin Receptor (IR). These inhibitors may potentially be used for treatment of cancer. | ||
| Protein kinases (PKs) possess activities that impact all aspects of cell life, such as cell growth, differentiation, and proliferation. Abnormal PK activities have been implicated in many diseases, ranging from psoriasis to glioblastoma (brain cancer). Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK)s are growth factor receptors that exhibit PK activity and perform diverse biological functions. There are at least nineteen identified different RTK classes; one of these classes includes insulin receptor (IR), insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-l R), and insulin receptor related receptor (IRR). Abnormal levels of IGF-l R and its ligands, IGF-1 and IGF-2, are expressed in many cancer tumors, such as breast, prostate, thyroid, lung, hepatoma, colon, brain, neuroendocrine, and other tumors. Inhibition of IGF-1 R is thus a promising therapeutic target for treatment of cancer. Known inhibitors of IGF-l R, such as the experimental drug BMS-754807, have been found to inhibit cancer growth in vitro, in vivo, and in clinical trials. The compounds represented by Formula (I) in this patent application which possess similar activities have the potential of providing a novel anticancer treatment. | |||
| Important Compound Classes: | 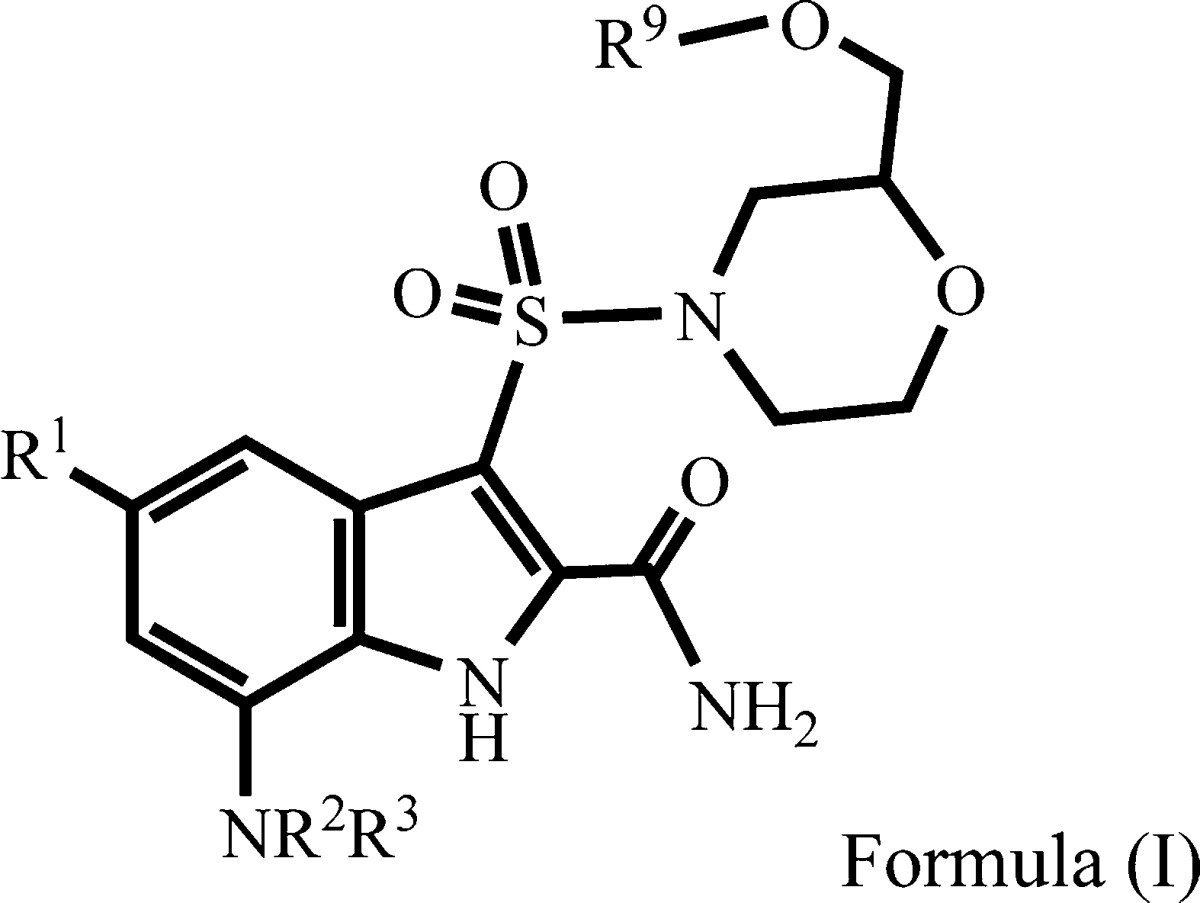 |
||
| Key Structures: | The patent application describes a list of 29 specific examples of
Formula (I), including compounds 19, 20,
and 34, illustrated below. All 29 compounds in the list
possess (S)-configurations.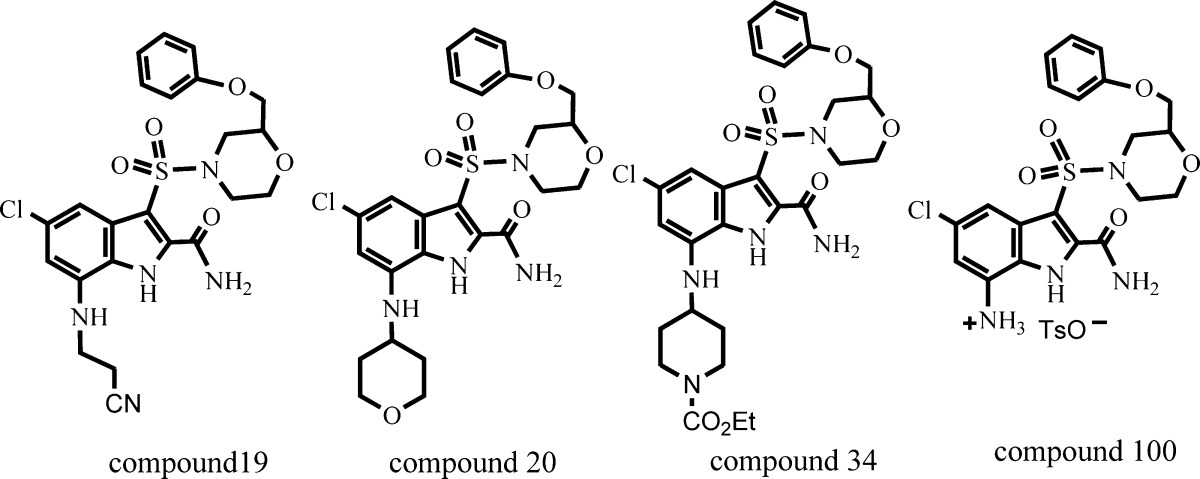
|
||
| Biological Assay: | The patent application described the following assays: | ||
| 1. In vitro IGF-lR and IR kinase assays: | |||
| 2. Antiproliferative assay | |||
| 3. CYP inhibition fluorescence assay | |||
| Biological Data: | The IC50 values were reported
for the antiproliferation activity of compounds 19, 20, 34, and 100 (structures above)
in colon cancer and breast cancer cell lines: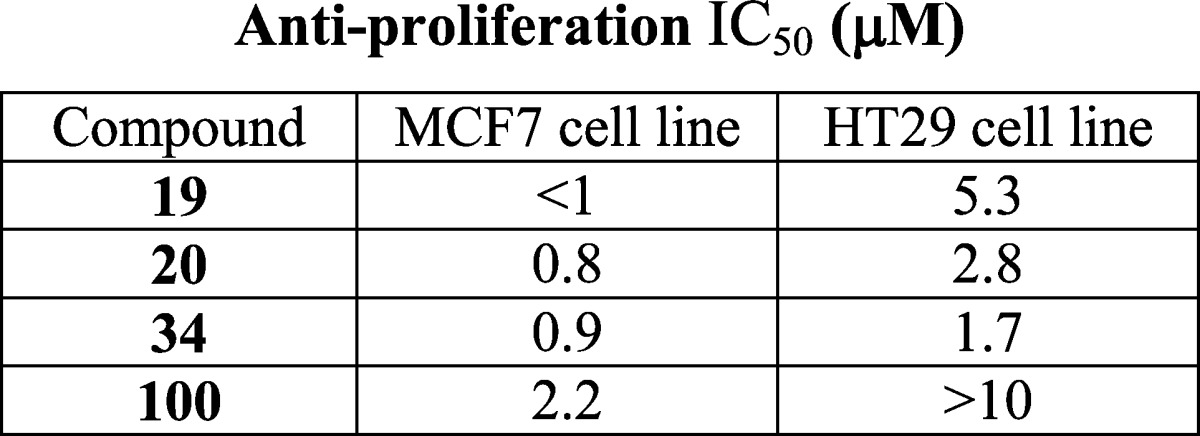
|
||
| Claims: | Claims 1–9: | Composition of matter; variations of Formula (I) | |
| Claim 10: | A group of 29 compounds listed by chemical name | ||
| Claims 10–13: | Three compounds (34, 19, and 20) listed by structures | ||
| Claim 14: | Pharmaceutical composition | ||
| Claim 15: | Compound for treatment of cancer | ||
| Recent Review Articles: | 1. Xue M.; Cao X.; Zhong Y.; Kuang D.; Liu X.; Zhao Z.; Li H.. Curr. Pharm. Des.2012, 18 (20), 2901–2913. | ||
| 2. Scagliotti G. V.; Novello S.. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2012, 38 (4), 292–302 | |||
| 3. Buck E.; Mulvihill M.. Expert Opin. Invest. Drugs 2011, 20 (5), 605–621. | |||
| Additional Information: | The patent application contains descriptions of the following two topics: | ||
| • Combination therapy: detailed description of other therapies that may be administered in combination with the compounds of the invention. | |||
| • Formulation | |||

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.