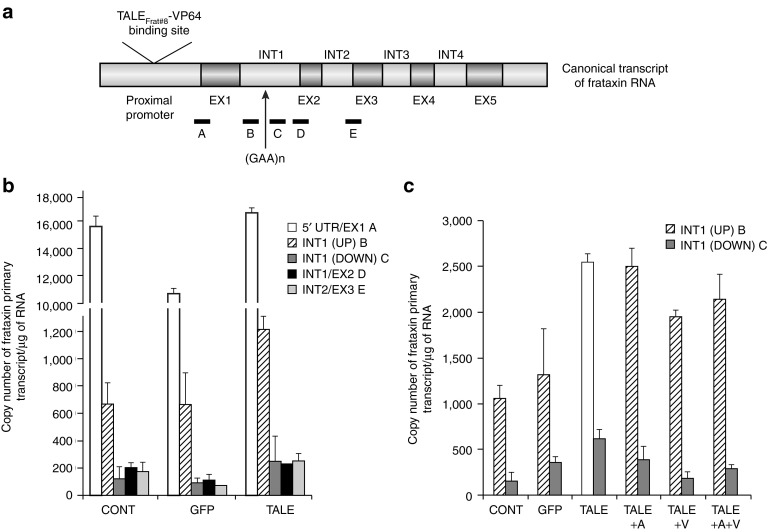
Figure 2.
TALEFrat-VP64 permits the elongation of the frataxin pre-mRNA in Friedreich ataxia (FRDA) fibroblasts. Fibroblasts from a FRDA patient were nucleofected with pCR3.1-TALEFrat#8–VP64. Control cells were either not nucleofected (CONT) or nucleofected with the pCR3.1-GFP plasmid (GFP). (a) Five different segments of the frataxin pre-mRNA were amplified by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR: segment A = 5′ UTR/exon 1; segment B = intron 1 before the GAA repeat INT1(UP); segment C = intron 1 after the GAA repeat INT1(DOWN); segment D = a junction of intron 1 and exon 2 (INT1/EX2), segment E = a junction of intron 2 and exon 3 (INT2/EX3) were quantified by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR. (b,c) The results are expressed as the number of copies of frataxin primary transcript per μg of RNA. The TALEFrat#8-VP64 significantly increased the elongation of the immature mRNA as indicated by the increased detection of fragments B to D. In c, the results are from a different experiment than in b, the pCR3.1-TALEFrat#8–VP64 increased the expression of segments B (INT1(UP)) and C (INT1(DOWN)). The addition of 5-Aza (A) or valproic acid (V) to the TALE treatment did not further increase the expression of the frataxin pre-mRNA. All results are based on duplicates and representative of at least two different experiments. GFP, green fluorescent protein; UTR, untranslated region.