Figure 4.
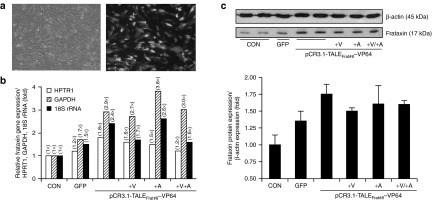
TALEFrat-VP64 increases the frataxin mRNA and the frataxin protein in Friedreich ataxia (FRDA) fibroblasts. The plasmid PCR3.1-TALEFrat#8–VP64 was nucleofected in FRDA fibroblasts. (a) Control cells were either not nucleofected (CONT) or nucleofected with a pCR3.1 plasmid coding for GFP. (b) The expression of the mature frataxin mRNA (i.e., the junction of exon 3 and exon 4) was quantified by reverse transcription-PCR. The results were normalized relative to three housekeeping genes (HPRT1, 18S rRNA, and GAPDH). The plasmid coding for the TALEFrat#8-VP64 increased the expression of frataxin more than the control plasmid coding for GFP. Valproic acid (V; 620 μmol/l), 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (A; 10 nmol/l) or a combination of both the drugs was added to the TALE treatment. Only 5-Aza further increased the frataxin expression but only when the results were normalized with the GAPDH mRNA. All results are based on duplicates. (c) The frataxin proteins from the same pool of cells as in b were quantified by western blot. The TALEFrat#8-VP64 alone increased the frataxin protein by 1.75-fold. However, the presence of valproic acid (+V) or 5-Aza (+A) alone or in combination did not result in an additional increase. All quantitative reverse transcription-PCR results are based on the three different experiments in duplicates. The western blot results are representative of two different experiments in duplicates. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GFP, green fluorescent protein; HPRT1, hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase 1; rRNA, ribosomal RNA.
