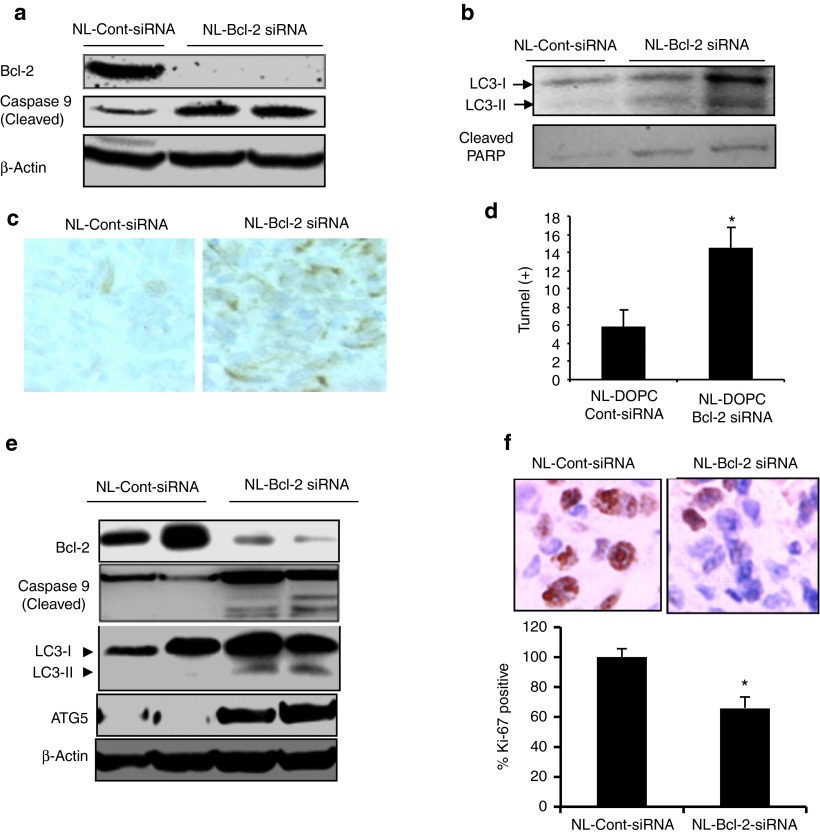
Figure 5.
In vivo silencing of Bcl-2 induces autophagy and apoptosis in ER(−) MDA-MB-231 tumors. (a) After 4 weeks treatment with NL-control siRNA or NL-Bcl-2 siRNA treatments, MDA-MB-231 tumors shown in Figure 3a were analyzed by western blot for detection activated/cleaved caspase-9 and PARP for evaluation of apopotosis. (b) Autophagy induction in MDA-MB-231 tumors was evidenced by detection of autophagy marker LC3-II in. (c) NL-Bcl-2-siRNA treatment-induced apoptosis was also shown by TUNEL staining of MDA-MB-231 tumors. (d) Quantification of TUNEL-positive cells in (c) shows that inhibition of Bcl-2 led to a threefold increase in apoptotic cells (P < 0.05). (e) Silencing of Bcl-2 expression by NL-Bcl-2-siRNA induced apoptosis and autophagy in MCF7 tumors. MCF tumors shown in Figure 4a were analyzed by western blot using specific antibodies to cleaved/activated caspase-9 for detection of apoptosis and LC3-II and ATG5 for detection of autophagy as described in the “Materials and Methods.” (f) NL-Bcl-2-siRNA treatment inhibited Ki-67 proliferation marker expression as indicated by immunohistochemistry (IHC). Ki-67 positive cells stained by IHC were quantified by counting five field from each tumor, indicating significant reduction of Ki-67 expression (*P < 0.05).