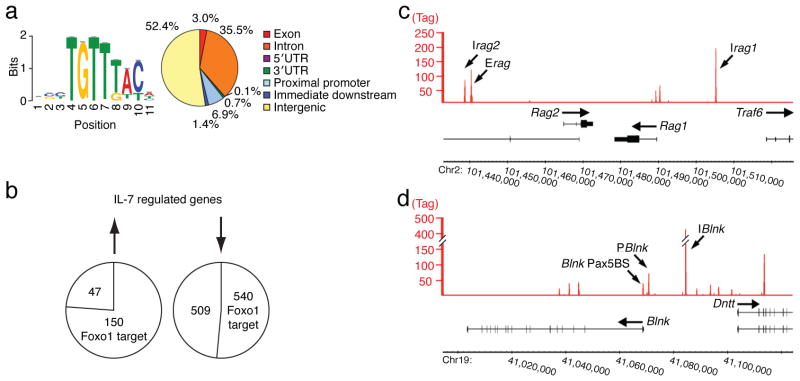
Figure 2. ChIPseq analysis of the Foxo1 cistrome in IRF-4,8−/− pre-B cells.
IRF-4,8−/− pre-B cells were cultured under IL-7 Lo conditions. Cross-linked and sheared chromatin was immunoprecipitated with αFoxo1 antibodies and then the eluted DNA was processed for massively parallel sequencing. (a) Left; De novo motif analysis of Foxo1 target sequences. 11,772 Foxo1 target sites were identified using QuEST. The target sequences associated with the top 500 Foxo1 peaks were analyzed using MEME to identify overrepresented motifs within +/− 100 bp from the peak maxima. Sequence logo depicts the Foxo1 motif (P-value for motif significance; P = 1.75E-6) that was present in all 500 sequences analyzed. Right; Genomic distribution of Foxo1 target sites was analyzed using Cis-regulatory Element Annotation System (CEAS). (b) Union analysis was used to compare the Foxo1 cistrome with IL-7 regulated genes identified by genome-wide expression analysis. The numbers within the circles indicate genes that are up regulated or down regulated by IL-7 signaling and also targeted by Foxo1. (c) and (d) Foxo1 binding peaks at the Rag1,2 and the Blnk, Dntt loci, respectively are depicted using Integrated Genome Browser (IGB). P and I denote Foxo1 binding peaks at promoter or intergenic regions, respectively. Pax5BS denotes a previously characterized Pax5 binding site19 that is also co-targeted by Foxo1. The y-axis shows the degree of target sequence enrichment in terms of normalized tag counts. Two independent ChIPseq experiments were performed.