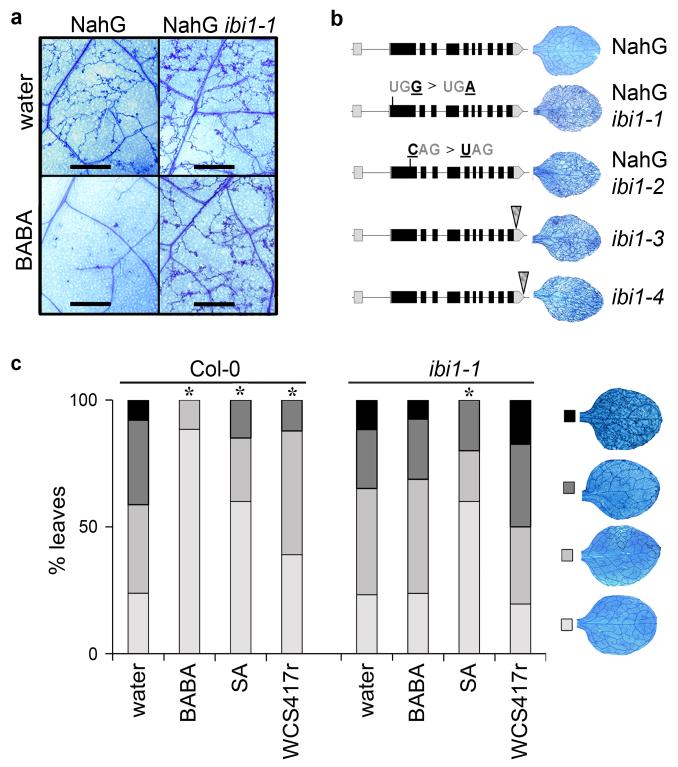
Figure 1. Identification and characterization of the Arabidopsis impaired in BABA-induced immunity1 (ibi1) mutant.
(a) The NahG ibi1-1 mutant does not express induced resistance against H. arabidopsidis WACO9 after root treatment with BABA (150 μM). Photographs of trypan-blue stained leaves show representative differences in pathogen colonization at 7 days after inoculation. Scale bar = 1 mm. (b) Genomic structure of IBI1 (At4g31180) and locations of ibi1-1 (EMS), ibi1-2 (EMS), ibi1-3 (T-DNA, SALK), and ibi1-4 (T-DNA, SAIL) mutations. Insets illustrate representative levels of H. arabidopsidis colonization in leaves of BABA-treated plants. (c) Levels of induced resistance against H. arabidopsidis WACO9 in Col-0 and ibi1-1 after root treatment with BABA (150 μM), Pseudomonas fluorescens WCS417r (5×107 cells/g. soil), or shoot treatment with SA (0.5 mM). Insets show different classes of pathogen colonization; asterisks indicate statistically significant differences in class distribution relative to water-treated plants (Fisher’s exact test, p<0.01, n=50-100).