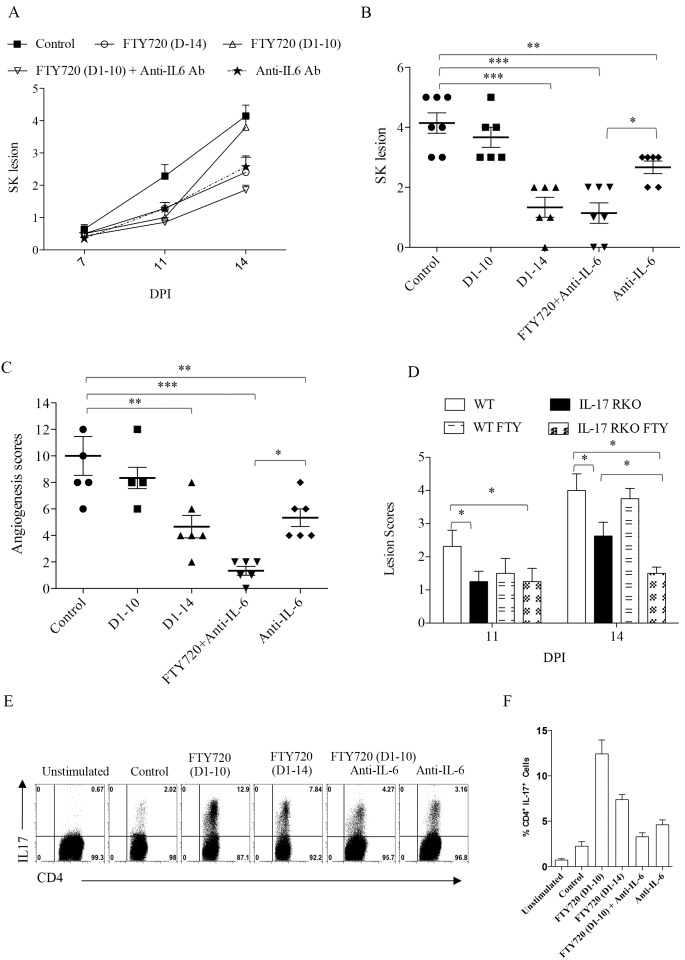
Figure 4. Inhibition of Th17 generation prevents recurrence of lesions in HSV-1 infected mice.
C57BL/6 and IL-17 RKO mice were infected with 1×104 PFU of HSV-1. First group of mice were left untreated which served as controls. Second group of mice received FTY720 starting from 24 hrs pi. until 14 days pi. Third group of mice received FTY720 until day 10 pi. and later FTY720 treatment was discontinued. Fourth group of mice received FTY720 until day 10 pi and this group was also treated with IL-6 neutralizing antibody every alternate day until the day 14 pi. Fifth group of mice received only IL-6 neutralizing antibody treatment every alternate day until the day 14 pi. and the disease progression was observed. (A) SK progression was measured in treated and control groups at different time points till day 15 pi. (B) SK lesion scores on day 15 pi. Statistical significance was calculated by one-way ANOVA (*p≤0.05, ** p≤0.01, and ***p≤0.001). (C) Angiogenesis scores were measured in anti-IL-6 Ab treated and control groups on day 15 pi. (n = 5 to 6 mice per group). (D) The comparative analysis of disease progression in WT and IL-17 RKO mice that were given FTY720 treatment or where treatment was withdrawn. SK lesion scores were measured on day 11 and 14 pi. in different groups of mice i.e., infected controls, infected control mice treated with FTY720 (0.3 mg/kg body wt) from day 1–10, IL-17RKO mice and IL-17 RKO mice treated from day 1–10 with FTY720 (0.3 mg/kg body wt) from day 1–10 pi. Per group five mice were used and the experiments were repeated twice. Statistical significance was calculated by one-way ANOVA (*p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, and ***p≤0.001). (E) FACS plots representing the frequencies of IL-17 producing cells isolated from draining lymph nodes of various groups and stimulated in the presence of PMA/Ionomycin. (F) Cumulative data for the production of Th17 in different groups of mice is represented by bar graphs.